The Impact of Systemic Inflammation on Alzheimer's Disease Pathology
- PMID: 35069578
- PMCID: PMC8770958
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.796867
The Impact of Systemic Inflammation on Alzheimer's Disease Pathology
Abstract
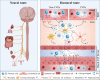
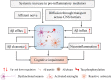
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a devastating age-related neurodegenerative disorder with an alarming increasing prevalence. Except for the recently FDA-approved Aducanumab of which the therapeutic effect is not yet conclusively proven, only symptomatic medication that is effective for some AD patients is available. In order to be able to design more rational and effective treatments, our understanding of the mechanisms behind the pathogenesis and progression of AD urgently needs to be improved. Over the last years, it became increasingly clear that peripheral inflammation is one of the detrimental factors that can contribute to the disease. Here, we discuss the current understanding of how systemic and intestinal (referred to as the gut-brain axis) inflammatory processes may affect brain pathology, with a specific focus on AD. Moreover, we give a comprehensive overview of the different preclinical as well as clinical studies that link peripheral Inflammation to AD initiation and progression. Altogether, this review broadens our understanding of the mechanisms behind AD pathology and may help in the rational design of further research aiming to identify novel therapeutic targets.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; gut-brain axis; neuroinflammation; peripheral inflammation; systemic inflammation.
Copyright © 2022 Xie, Van Hoecke and Vandenbroucke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

