Building a Barrier: The Influence of Different Wax Fractions on the Water Transpiration Barrier of Leaf Cuticles
- PMID: 35069622
- PMCID: PMC8766326
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2021.766602
Building a Barrier: The Influence of Different Wax Fractions on the Water Transpiration Barrier of Leaf Cuticles
Abstract
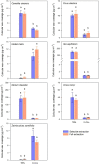
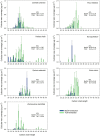
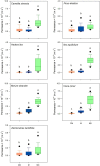
Waxes are critical in limiting non-stomatal water loss in higher terrestrial plants by making up the limiting barrier for water diffusion across cuticles. Using a differential extraction protocol, we investigated the influence of various wax fractions on the cuticular transpiration barrier. Triterpenoids (TRPs) and very long-chain aliphatics (VLCAs) were selectively extracted from isolated adaxial leaf cuticles using methanol (MeOH) followed by chloroform (TCM). The water permeabilities of the native and the solvent-treated cuticles were measured gravimetrically. Seven plant species (Camellia sinensis, Ficus elastica, Hedera helix, Ilex aquifolium, Nerium oleander, Vinca minor, and Zamioculcas zamiifolia) with highly varying wax compositions ranging from nearly pure VLCA- to TRP-dominated waxes were selected. After TRP removal with MeOH, water permeability did not or only slightly increase. The subsequent VLCA extraction with TCM led to increases in cuticular water permeabilities by up to two orders of magnitude. These effects were consistent across all species investigated, providing direct evidence that the cuticular transpiration barrier is mainly composed of VLCA. In contrast, TRPs play no or only a minor role in controlling water loss.
Keywords: leaf cuticles; leaf cuticular wax properties; non-stomatal transpiration; selective wax extraction; triterpenoids; very long-chain aliphatics; weighted average chain length.
Copyright © 2022 Seufert, Staiger, Arand, Bueno, Burghardt and Riederer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Becker M., Kerstiens G., Schönherr J. (1986). Water permeability of plant cuticles: permeance, diffusion and partition coefficients. Trees - Struct. Funct. 1, 54–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00197025 - DOI
-
- Bueno A., Sancho-Knapik D., Gil-Pelegrín E., Leide J., Peguero-Pina J. J., Burghardt M., et al. . (2020). Cuticular wax coverage and its transpiration barrier properties in Quercus coccifera L. leaves: does the environment matter? Tree Physiol. 40, 827–840. doi: 10.1093/treephys/tpz110, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Burghardt M., Riederer M. (2006). “Cuticular transpiration,” in Biology of the Plant Cuticle. eds. Riederer M., Müller C. (Oxford: Blackwell Publishing; ), 291–310.
-
- Busta L., Reinhard J. (2018). Moving beyond the ubiquitous: the diversity and biosynthesis of specialty compounds in plant cuticular waxes. Phytochem. Rev. 17, 1275–1304. doi: 10.1007/s11101-017-9542-0 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

