Lectin-type oxidized LDL receptor 1 modulates matrix metalloproteinase 2 production in peri-implantitis
- PMID: 35069852
- PMCID: PMC8764579
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2021.11094
Lectin-type oxidized LDL receptor 1 modulates matrix metalloproteinase 2 production in peri-implantitis
Abstract
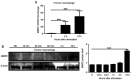
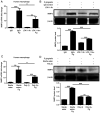
Peri-implantitis is a disease in which inflammatory lesions that affect the surrounding soft and hard tissues develop. Matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2) is hypothesized to be involved in this destructive process. However, the regulatory mechanism of action of MMP2 in the peripheral tissues of the implant are not fully understood. To determine the expression of MMP2 in peri-implantitis, peri-implant crevicular fluid (PICF) was collected from patients with peri-implantitis. The healthy volunteers' peripheral blood human macrophages infected with Porphyromonas gingivalis (P. gingivalis) were used as a cell model to explore the regulatory mechanism of MMP2 regarding dental implants. Western blotting, reverse transcription-quantitative PCR and immunofluorescence staining were used to measure the expression of MMP2 in the present study. MMP2 expression was increased in the PICF of the patients with peri-implantitis and in human macrophages infected with P. gingivalis. Lectin-type oxidized LDL receptor 1 (LOX-1) mediated the expression of MMP2 in human macrophages upon infection of P. gingivalis, whereas dendritic cell-associated c-type lectin-1 did not appear to be involved in this regulatory process. However, JNK and ERK1/2 were involved in P. gingivalis induced MMP2 expression. The results of this study showed that MMP2 was involved in peri-implantitis. MMP2 was upregulated by LOX-1 in a JNK and ERKk1/2 signaling dependent manner in the cell model. The LOX-1/MMP2 signaling pathway may thus be a potential target for management of peri-implantitis.
Keywords: Porphyromonas gingivalis; lectin-type oxidized LDL receptor 1; matrix metalloproteinase 2; peri-implantitis.
Copyright © 2020, Spandidos Publications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
LOX-1 is involved in IL-1β production and extracellular matrix breakdown in dental peri-implantitis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2017 Nov;52:127-135. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2017.09.003. Epub 2017 Oct 12. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28898769
-
Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 is Regulated by LOX-1 and erk1/2 Pathway in Dental Peri-Implantitis.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2020;21(9):862-871. doi: 10.2174/1389201021666200221121139. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32081107
-
LOX-1 is involved in TLR2 induced RANKL regulation in peri-implantitis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 Dec;77:105956. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105956. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31655342
-
Proinflammatory cytokines in the crevicular fluid of patients with peri-implantitis.Cytokine. 2011 Jan;53(1):8-12. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2010.08.013. Epub 2010 Sep 25. Cytokine. 2011. PMID: 20870421 Review.
-
The Role of Caspase-11 and Pyroptosis in the Regulation of Inflammation in Peri-Implantitis.J Inflamm Res. 2023 Oct 10;16:4471-4479. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S427523. eCollection 2023. J Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 37842190 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 by Porphyromonas gingivalis promoting progression of atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-/- mice.J Dent Sci. 2025 Apr;20(2):754-763. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2024.10.015. Epub 2024 Oct 30. J Dent Sci. 2025. PMID: 40224117 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Potential Therapeutic Approach Using Ginsenosides for the Management of Neurodegenerative Disorders.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Jul;66(7):1520-1536. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00783-2. Epub 2023 Jun 18. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37330923 Review.
-
Alveolar Epithelial Type 2 Cell Dysfunction in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Lung. 2022 Oct;200(5):539-547. doi: 10.1007/s00408-022-00571-w. Epub 2022 Sep 22. Lung. 2022. PMID: 36136136 Review.
References
-
- Barootchi S, Wang HL. Peri-implant diseases: Current understanding and management. Int J Oral Implantol (Berl) 2021;14:263–282. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
