Leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin-2 and fibroblast growth factor 21 in alcohol-induced liver cirrhosis
- PMID: 35070009
- PMCID: PMC8727211
- DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i12.2071
Leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin-2 and fibroblast growth factor 21 in alcohol-induced liver cirrhosis
Abstract
Background: The importance of early diagnosis of alcoholic liver disease underscores the need to seek better and especially non-invasive diagnostic procedures. Leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin-2 (LECT2) has been widely studied to determine its usefulness in monitoring the course of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease but not for alcoholic liver cirrhosis (ALC).
Aim: To determine the concentration of LECT2 in the blood serum of patients in relation to progressive stages of ALC, its relation to fibroblast growth factor 1 (FGF-1) and FGF-21, and to examine the possible wider use of LECT2 in diagnosing ALC.
Methods: A retrospective case-control study was conducted with 69 ALC cases and 17 controls with no ALC. Subjects were recruited from the region of Lublin (eastern Poland). Liver cirrhosis was diagnosed based on clinical features, history of heavy alcohol consumption, laboratory tests, and abdominal ultrasonography. The degree of ALC was evaluated according to Pugh-Child criteria (the Pugh-Child score). Blood was drawn and, after centrifugation, serum was collected for analysis. LECT2, FGF-1, and FGF-21 were determined using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits.
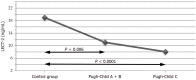
Results: The LECT2 Levels in the control group were 18.99 ± 5.36 ng/mL. In the study groups, they declined with the progression of cirrhosis to 11.06 ± 6.47 ng/mL in one group and to 8.06 ± 5.74 ng/mL in the other (P < 0.0001). Multiple comparison tests confirmed the statistically significant differences in LECT2 Levels between the control group and both test groups (P = 0.006 and P < 0.0001). FGF-21 Levels were 44.27 ± 64.19 pg/mL in the first test group, 45.4 ± 51.69 pg/mL in the second (P = 0.008), and 13.52 ± 7.51 pg/mL in the control group. The difference between the control group and the second test group was statistically significant (P = 0.007).
Conclusion: We suggest that LECT2 may be a non-invasive diagnostic factor for alcohol-induced liver cirrhosis. The usefulness of LECT2 for non-invasive monitoring of alcohol-induced liver cirrhosis was indirectly confirmed by the multiple regression model developed on the basis of our statistical analysis.
Keywords: Alcoholic liver cirrhosis; Fibroblast growth factor 1; Fibroblast growth factor 21; Leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin-2; Pugh-Child score.
©The Author(s) 2021. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The emerging roles of leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin-2 in immune diseases: From mechanisms to therapeutic potential.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 9;14:1158083. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1158083. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36969200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin 2 correlates with pediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Clin Transl Sci. 2023 Dec;16(12):2719-2728. doi: 10.1111/cts.13666. Epub 2023 Oct 27. Clin Transl Sci. 2023. PMID: 37877453 Free PMC article.
-
Activity of MMP-2, MMP-8 and MMP-9 in serum as a marker of progression of alcoholic liver disease in people from Lublin Region, eastern Poland.Ann Agric Environ Med. 2015;22(2):325-8. doi: 10.5604/12321966.1152088. Ann Agric Environ Med. 2015. PMID: 26094532
-
Serum leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin 2 level is associated with atopic dermatitis patients.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Oct;10(10):11006-11012. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-2690. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 34763463
-
Hepatokines and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Acta Biochim Pol. 2016;63(3):459-67. doi: 10.18388/abp.2016_1252. Epub 2016 Jun 6. Acta Biochim Pol. 2016. PMID: 27262842 Review.
Cited by
-
The emerging roles of leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin-2 in immune diseases: From mechanisms to therapeutic potential.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 9;14:1158083. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1158083. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36969200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LECT2: A pleiotropic and promising hepatokine, from bench to bedside.J Cell Mol Med. 2022 Jul;26(13):3598-3607. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17407. Epub 2022 Jun 3. J Cell Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35656863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of LECT2 in exacerbating atopic dermatitis: insight from in vivo and in vitro models via NF-κB signaling pathway.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 14;15:1439367. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1439367. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39206203 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sato M, Kamada Y, Takeda Y, Kida S, Ohara Y, Fujii H, Akita M, Mizutani K, Yoshida Y, Yamada M, Hougaku H, Takehara T, Miyoshi E. Fetuin-A negatively correlates with liver and vascular fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease subjects. Liver Int. 2015;35:925–935. - PubMed
-
- Celebi G, Genc H, Gurel H, Sertoglu E, Kara M, Tapan S, Acikel C, Karslioglu Y, Ercin CN, Dogru T. The relationship of circulating fetuin-a with liver histology and biomarkers of systemic inflammation in nondiabetic subjects with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:139–145. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous