Urine Biomarkers Combined With Ultrasound for the Diagnosis of Obstruction in Pediatric Hydronephrosis
- PMID: 35071129
- PMCID: PMC8771629
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2021.762417
Urine Biomarkers Combined With Ultrasound for the Diagnosis of Obstruction in Pediatric Hydronephrosis
Abstract
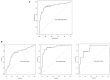
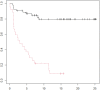
Introduction: To establish the efficacy of ultrasound (US) combined with urine biomarkers in differentiating patients who require surgical management from those who do not, avoiding invasive investigations. Materials and Methods: From February 2019 to February 2021, all pediatric patients who presented with hydronephrosis were selected for the study. All renal units (RU) were evaluated by US, and fresh frozen voided urine samples were collected at the time of inclusion. Hydronephrosis grade was evaluated by the Society for Fetal Urology (SFU) and an alternative grading system (AGS). Patients who had high-grade hydronephrosis on US were referred to renal scan (RS) or intervention, when there was an increase of dilatation in subsequent follow-up images. Fresh frozen urine from the control group with no history of renal diseases and no renal anomalies on US was collected. We compared differences of US parameters combined with urine biomarkers between surgically and non-surgically managed patients and between the groups of patients when they were stratified by different RS findings and analyzed whether urinary biomarkers give any additional value to US. Instead of the anterior-posterior diameter (APD), we used its ratio with mid-parenchymal thickness. The additional efficacy of biomarkers to US was calculated when the US component was derived to a cumulative APD/mid-parenchymal ratio. Results: Sixty-four patients with hydronephrosis were prospectively included in the study accounting for a total of 81 patient visits and 162 RUs evaluated. A control group of 26 patients was collected. The mean age at inclusion in the hydronephrosis group was 43.7(±45.5) months, and a mean age in a control group was 61.2(±41.3) months. The cumulative APD/mid-parenchymal ratio combined with urinary albumin, β2 microglobulin (β2-M), and urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalcin may have a better performance in the prediction of surgical intervention than the cumulative APD/mid-parenchymal ratio alone (p = 0.1). The best performance to detect the increased tissue transit time and obstructive curve on RS was demonstrated by the β2-M creatinine ratio. An increased cumulative APD/mid-parenchymal ratio with biomarkers together had a fairly good sensitivity and specificity for detection of DRF < 40%. Conclusions: According to our data, the APD/mid-parenchymal ratio alone has good efficacy in prediction of surgery and abnormal RS findings especially when combined with urine biomarkers.
Keywords: hydronephrosis; renal scan; ultrasound; ureteropelvic junction obstruction; urine biomarkers.
Copyright © 2022 Kazlauskas, Bilius, Jakutis, Komiagiene, Burnyte and Verkauskas.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Predictors for the need of surgery in antenatally detected hydronephrosis due to UPJ obstruction--a prospective multivariate analysis.J Pediatr Urol. 2015 Oct;11(5):248.e1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2015.02.008. Epub 2015 Mar 13. J Pediatr Urol. 2015. PMID: 25986208
-
Diagnostic accuracy of renal pelvic dilatation for detecting surgically managed ureteropelvic junction obstruction.J Urol. 2013 Aug;190(2):661-6. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2013.02.014. Epub 2013 Feb 14. J Urol. 2013. PMID: 23416643
-
Changes in differential renal function after pyeloplasty in infants and children.J Pediatr Urol. 2020 Jun;16(3):329.e1-329.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2020.02.002. Epub 2020 Feb 11. J Pediatr Urol. 2020. PMID: 32146062
-
Urinary biomarkers in hydronephrosis.Dan Med J. 2013 Feb;60(2):B4582. Dan Med J. 2013. PMID: 23461995 Review.
-
Grading of Hydronephrosis: An Ongoing Challenge.Front Pediatr. 2020 Aug 27;8:458. doi: 10.3389/fped.2020.00458. eCollection 2020. Front Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32984198 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Artificial Intelligence Tools in Pediatric Urology: A Comprehensive Review of Recent Advances.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Sep 17;14(18):2059. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14182059. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39335738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of tissue fibrosis genes in congenitally obstructed pyeloureteral junction and biomarkers of renal damage.Cent European J Urol. 2024;77(2):326-333. doi: 10.5173/ceju.2023.218R. Epub 2024 Feb 25. Cent European J Urol. 2024. PMID: 39345321 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Duong HP, Piepsz A, Khelif K, Collier F, de Man K, Damry N, et al. . Transverse comparisons between ultrasound and radionuclide parameters in children with presumed antenatally detected pelvi-ureteric junction obstruction. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2015) 42:940–6. 10.1007/s00259-014-2965-6 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

