Facing Diseases Caused by Trypanosomatid Parasites: Rational Design of Pd and Pt Complexes With Bioactive Ligands
- PMID: 35071192
- PMCID: PMC8777014
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2021.816266
Facing Diseases Caused by Trypanosomatid Parasites: Rational Design of Pd and Pt Complexes With Bioactive Ligands
Abstract
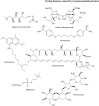
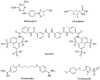
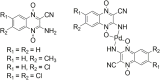
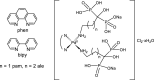
Human African Trypanosomiasis (HAT), Chagas disease or American Trypanosomiasis (CD), and leishmaniases are protozoan infections produced by trypanosomatid parasites belonging to the kinetoplastid order and they constitute an urgent global health problem. In fact, there is an urgent need of more efficient and less toxic chemotherapy for these diseases. Medicinal inorganic chemistry currently offers an attractive option for the rational design of new drugs and, in particular, antiparasitic ones. In this sense, one of the main strategies for the design of metal-based antiparasitic compounds has been the coordination of an organic ligand with known or potential biological activity, to a metal centre or an organometallic core. Classical metal coordination complexes or organometallic compounds could be designed as multifunctional agents joining, in a single molecule, different chemical species that could affect different parasitic targets. This review is focused on the rational design of palladium(II) and platinum(II) compounds with bioactive ligands as prospective drugs against trypanosomatid parasites that has been conducted by our group during the last 20 years.
Keywords: antiparasitic agents; palladium; platinum; rational design; trypanosomatid parasites.
Copyright © 2022 Gambino and Otero.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
New Pd-Fe ferrocenyl antiparasitic compounds with bioactive 8-hydroxyquinoline ligands: a comparative study with their Pt-Fe analogues.Dalton Trans. 2021 Feb 7;50(5):1651-1665. doi: 10.1039/d0dt03963b. Epub 2021 Jan 15. Dalton Trans. 2021. PMID: 33449983
-
Multifunctional Organometallic Compounds Active against Infective Trypanosomes: Ru(II) Ferrocenyl Derivatives with Two Different Bioactive Ligands.Inorg Chem. 2024 Jun 24;63(25):11667-11687. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.4c01125. Epub 2024 Jun 11. Inorg Chem. 2024. PMID: 38860314
-
Organometallic compounds in the discovery of new agents against kinetoplastid-caused diseases.Eur J Med Chem. 2018 Jul 15;155:459-482. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.05.044. Epub 2018 Jun 1. Eur J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29908440 Review.
-
Metal Compounds in the Development of Antiparasitic Agents: Rational Design from Basic Chemistry to the Clinic.Met Ions Life Sci. 2019 Jan 14;19:/books/9783110527872/9783110527872-019/9783110527872-019.xml. doi: 10.1515/9783110527872-019. Met Ions Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30855114 Review.
-
New multifunctional Ru(II) organometallic compounds show activity against Trypanosoma brucei and Leishmania infantum.J Inorg Biochem. 2022 Dec;237:112016. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2022.112016. Epub 2022 Oct 3. J Inorg Biochem. 2022. PMID: 36244312
Cited by
-
5-Nitrofuryl-Containing Thiosemicarbazone Gold(I) Compounds: Synthesis, Stability Studies, and Anticancer Activity.Chempluschem. 2023 Dec;88(12):e202300115. doi: 10.1002/cplu.202300115. Epub 2023 May 16. Chempluschem. 2023. PMID: 37191319 Free PMC article.
-
A novel palladium complex with a coumarin-thiosemicarbazone hybrid ligand inhibits Trypanosoma cruzi release from host cells and lowers the parasitemia in vivo.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2023 Dec;28(8):711-723. doi: 10.1007/s00775-023-02020-2. Epub 2023 Sep 28. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2023. PMID: 37768364
-
Special Issue: "Rational Design and Synthesis of Bioactive Molecules".Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 14;25(18):9927. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189927. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337415 Free PMC article.
-
Metallomics: An Essential Tool for the Study of Potential Antiparasitic Metallodrugs.ACS Omega. 2024 Mar 25;9(14):15744-15752. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c10200. eCollection 2024 Apr 9. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38617611 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aguirre G., Boiani L., Cerecetto H., González M., Denicola A., Otero L., et al. (2004). In Vitro activity and Mechanism of Action against the Protozoan Parasite Trypanosoma Cruzi of 5-nitrofuryl Containing Thiosemicarbazones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 12, 4885–4893. 10.1016/j.bmc.2004.07.003 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Allardyce C. S., Dorcier A., Scolaro C., Dyson P. J. (2005). Development of Organometallic (Organo-Transition Metal) Pharmaceuticals. Appl. Organometal. Chem. 19, 1–10. 10.1002/aoc.725 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

