A Polyhydroxyalkanoates-Based Carrier Platform of Bioactive Substances for Therapeutic Applications
- PMID: 35071207
- PMCID: PMC8767415
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.798724
A Polyhydroxyalkanoates-Based Carrier Platform of Bioactive Substances for Therapeutic Applications
Abstract
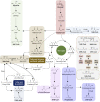
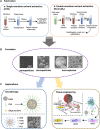
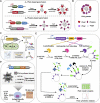
Bioactive substances (BAS), such as small molecule drugs, proteins, RNA, cells, etc., play a vital role in many therapeutic applications, especially in tissue repair and regeneration. However, the therapeutic effect is still a challenge due to the uncontrollable release and instable physico-chemical properties of bioactive components. To address this, many biodegradable carrier systems of micro-nano structures have been rapidly developed based on different biocompatible polymers including polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), the microbial synthesized polyesters, to provide load protection and controlled-release of BAS. We herein highlight the developments of PHA-based carrier systems in recent therapeutic studies, and give an overview of its prospective applications in various disease treatments. Specifically, the biosynthesis and material properties of diverse PHA polymers, designs and fabrication of micro- and nano-structure PHA particles, as well as therapeutic studies based on PHA particles, are summarized to give a comprehensive landscape of PHA-based BAS carriers and applications thereof. Moreover, recent efforts focusing on novel-type BAS nano-carriers, the functionalized self-assembled PHA granules in vivo, was discussed in this review, proposing the underlying innovations of designs and fabrications of PHA-based BAS carriers powered by synthetic biology. This review outlines a promising and applicable BAS carrier platform of novelty based on PHA particles for different medical uses.
Keywords: bioactive substances; carrier platform; drug delivery; polyhydroxyalkanoates; self-assembled PHA granules; therapeutic applications.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Liu, Yang, Chen, Lin, Han, Cao, Zeng and Ye.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Biodegradable and Biocompatible Polyhydroxy-alkanoates (PHA): Auspicious Microbial Macromolecules for Pharmaceutical and Therapeutic Applications.Molecules. 2018 Feb 8;23(2):362. doi: 10.3390/molecules23020362. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29419813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoate granules: biogenesis, structure, and potential use as nano-/micro-beads in biotechnological and biomedical applications.Biomacromolecules. 2009 Apr 13;10(4):660-9. doi: 10.1021/bm801394s. Biomacromolecules. 2009. PMID: 19275166 Review.
-
Recent advances of using polyhydroxyalkanoate-based nanovehicles as therapeutic delivery carriers.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2017 May;9(3). doi: 10.1002/wnan.1429. Epub 2016 Sep 6. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2017. PMID: 27595635 Review.
-
Film forming microbial biopolymers for commercial applications--a review.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2014 Dec;34(4):338-57. doi: 10.3109/07388551.2013.798254. Epub 2013 Aug 6. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 23919238 Review.
-
Polyhydroxyalkanoates, bacterially synthesized polymers, as a source of chemical compounds for the synthesis of advanced materials and bioactive molecules.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Oct;105(20):7555-7566. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11589-0. Epub 2021 Sep 18. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34536102 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Carbon:Nitrogen Ratio Affects Differentially the Poly-β-hydroxybutyrate Synthesis in Bacillus thuringiensis Isolates from México.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Jul 18;17(14):1978. doi: 10.3390/polym17141978. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40732855 Free PMC article.
-
Polyhydroxyalkanoate Decelerates the Release of Paclitaxel from Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) Nanoparticles.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Aug 2;14(8):1618. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14081618. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36015244 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of Microparticles Based on Resorbable Polyhydroxyalkanoates Loaded with Antibacterial and Cytostatic Drugs.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 7;24(19):14983. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914983. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834429 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Recent Developments in Biopolymer Nano-Based Drug Delivery Systems with Antioxidative Properties: Insights into the Last Five Years.Pharmaceutics. 2024 May 16;16(5):670. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16050670. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38794332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advanced drug delivery and therapeutic strategies for tuberculosis treatment.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Nov 9;21(1):414. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-02156-y. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 37946240 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

