A Novel Three-Dimensional Computational Method to Assess Rod Contour Deformation and to Map Bony Fusion in a Lumbopelvic Reconstruction After En-Bloc Sacrectomy
- PMID: 35071306
- PMCID: PMC8766313
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2021.698179
A Novel Three-Dimensional Computational Method to Assess Rod Contour Deformation and to Map Bony Fusion in a Lumbopelvic Reconstruction After En-Bloc Sacrectomy
Abstract
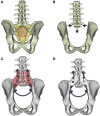
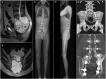
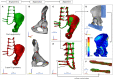
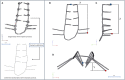
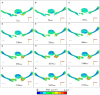
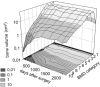
Introduction: En-bloc resection of a primary malignant sacral tumor with wide oncological margins impacts the biomechanics of the spinopelvic complex, deteriorating postoperative function. The closed-loop technique (CLT) for spinopelvic fixation (SPF) uses a single U-shaped rod to restore the spinopelvic biomechanical integrity. The CLT method was designed to provide a non-rigid fixation, however this hypothesis has not been previously tested. Here, we establish a computational method to measure the deformation of the implant and characterize the bony fusion process based on the 6-year follow-up (FU) data. Materials and Methods: Post-operative CT scans were collected of a male patient who underwent total sacrectomy at the age of 42 due to a chordoma. CLT was used to reconstruct the spinopelvic junction. We defined the 3D geometry of the implant construct. Using rigid registration algorithms, a common coordinate system was created for the CLT to measure and visualize the deformation of the construct during the FU. In order to demonstrate the cyclical loading of the construct, the patient underwent gait analysis at the 6th year FU. First, a region of interest (ROI) was selected at the proximal level of the construct, then the deformation was determined during the follow-up period. In order to investigate the fusion process, a single axial slice-based voxel finite element (FE) mesh was created. The Hounsfield values (HU) were determined, then using an empirical linear equation, bone mineral density (BMD) values were assigned for every mesh element, out of 10 color-coded categories (1st category = 0 g/cm3, 10th category 1.12 g/cm3). Results: Significant correlation was found between the number of days postoperatively and deformation in the sagittal plane, resulting in a forward bending tendency of the construct. Volume distributions were determined and visualized over time for the different BMD categories and it was found that the total volume of the elements in the highest BMD category in the first postoperative CT was 0.04 cm3, at the 2nd year, FU was 0.98 cm3, and after 6 years, it was 2.30 cm3. Conclusion: The CLT provides a non-rigid fixation. The quantification of implant deformation and bony fusion may help understate the complex lumbopelvic biomechanics after sacrectomy.
Keywords: biomechanics; bone mineral density; bony fusion; computational method; computed tomography; implant deformation; lumbopelvic reconstruction; sacrectomy.
Copyright © 2022 Eltes, Turbucz, Fayad, Bereczki, Szőke, Terebessy, Lacroix, Varga and Lazary.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The biomechanical effect of lumbopelvic distance reduction on reconstruction after total sacrectomy: a comparative finite element analysis of four techniques.Spine J. 2024 Oct;24(10):1981-1992. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2024.04.024. Epub 2024 Apr 28. Spine J. 2024. PMID: 38688331
-
A novel three dimensional-printed biomechanically evaluated patient-specific sacral implant in spinopelvic reconstruction after total en bloc sacrectomy.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 May 5;11:1153801. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1153801. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37214294 Free PMC article.
-
Compassionate use of a custom 3D-printed sacral implant for revision of failing sacrectomy: case report.J Neurosurg Spine. 2020 May 22;33(4):513-518. doi: 10.3171/2020.3.SPINE191497. Print 2020 Oct 1. J Neurosurg Spine. 2020. PMID: 32442976
-
Surgical techniques for total sacrectomy and spinopelvic reconstruction.Neurosurg Focus. 2003 Aug 15;15(2):E5. doi: 10.3171/foc.2003.15.2.5. Neurosurg Focus. 2003. PMID: 15350036 Review.
-
Total sacrectomy and Galveston L-rod reconstruction for malignant neoplasms. Technical note.J Neurosurg. 1997 Nov;87(5):781-7. doi: 10.3171/jns.1997.87.5.0781. J Neurosurg. 1997. PMID: 9347991 Review.
Cited by
-
Surgical and Oncologic Outcome following Sacrectomy for Primary Malignant Bone Tumors and Locally Recurrent Rectal Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jun 26;16(13):2334. doi: 10.3390/cancers16132334. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39001396 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

