The "Defibrillation Testing, Why Not?" survey. Testing of subcutaneous and transvenous defibrillators in the Italian clinical practice
- PMID: 35071727
- PMCID: PMC8761693
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2022.100952
The "Defibrillation Testing, Why Not?" survey. Testing of subcutaneous and transvenous defibrillators in the Italian clinical practice
Abstract
Background: Defibrillation testing (DT) can be omitted in patients undergoing transvenous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (T-ICD) implantation, but it is still recommended for patients at risk for a high defibrillation threshold and for ICD generator changes. Moreover, DT is still recommended on implantation of subcutaneous ICD (S-ICD). The aim of the present survey was to analyze the current practice of DT during T-ICD and S-ICD implantations.
Methods: In March 2021, an ad hoc questionnaire on the current performance of DT and the standard practice adopted during testing was completed at 72 Italian centers implanting S-ICD and T-ICD.
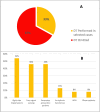
Results: 48 (67%) operators reported never performing DT during de-novo T-ICD implantations, while no operators perform it systematically. The remaining respondents perform it for patients at risk for a high defibrillation threshold. DT is never performed at T-ICD generator change. At the time of de-novo S-ICD implantation, DT is never performed by 9 (13%) operators and performed systematically by 48 (66%). The remaining operators frequently omit DT in patients with more severe systolic dysfunction. DT is not performed at S-ICD generator change by 92% of operators. DT is conducted by delivering a first shock energy of 65 J by 60% of operators, while the remaining 40% test lower energy values.
Conclusions: In current clinical practice, most operators omit DT at T-ICD implantation, even when still recommended in the guidelines. DT is also frequently omitted at S-ICD implantation, and a wide variability exists among operators in the procedures followed during DT.
Keywords: Defibrillation testing; Implantable defibrillator; Subcutaneous; Survey.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Healey J.S., Hohnloser S.H., Glikson M., Neuzner J., Mabo P., Vinolas X., Kautzner J., O'Hara G., VanErven L., Gadler F., Pogue J., Appl U., Gilkerson J., Pochet T., Stein K.M., Merkely B., Chrolavicius S., Meeks B., Foldesi C., Thibault B., Connolly S.J. Shockless IMPLant Evaluation [SIMPLE] investigators. Cardioverter defibrillator implantation without induction of ventricular fibrillation: a single-blind, non-inferiority, randomised controlled trial (SIMPLE) Lancet. 2015;385(9970):785–791. - PubMed
-
- Bänsch D., Bonnemeier H., Brandt J., Bode F., Svendsen J.H., Táborský M., Kuster S., Blomström-Lundqvist C., Felk A., Hauser T., Suling A., Wegscheider K., NORDIC ICD Trial Investigators Intra-operative defibrillation testing and clinical shock efficacy in patients with implantable cardioverter-defibrillators: the NORDIC ICD randomized clinical trial. Eur. Heart J. 2015;36(37):2500–2507. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brignole M., Occhetta E., Bongiorni M.G., Proclemer A., Favale S., Iacopino S., Calò L., Vado A., Buja G., Mascioli G., Quartieri F., Tritto M., Parravicini U., Castro A., Tomasi C., Villani G.Q., D'Acri M.G., Klersy C., Gasparini M. Clinical evaluation of defibrillation testing in an unselected population of 2,120 consecutive patients undergoing first implantable cardioverter-defibrillator implant. J. Am. Coll Cardiol. 2012;60(11):981–987. - PubMed
-
- Wilkoff B.L., Fauchier L., Stiles M.K., Morillo C.A., Al-Khatib S.M., Almendral J., Aguinaga L., Berger R.D., Cuesta A., Daubert J.P., Dubner S., Ellenbogen K.A., Estes N.A.M., Fenelon G., Garcia F.C., Gasparini M., Haines D.E., Healey J.S., Hurtwitz J.L., Keegan R., Kolb C., Kuck K.-H., Marinskis G., Martinelli M., Mcguire M., Molina L.G., Okumura K., Proclemer A., Russo A.M., Singh J.P., Swerdlow C.D., Teo W.S., Uribe W., Viskin S., Wang C.-C., Zhang S. HRS/EHRA/APHRS/SOLAECE expert consensus statement on optimal implantable cardioverter-defibrillator programming and testing. Europace. 2016;18(2):159–183. - PubMed
-
- Weiss R., Knight B.P., Gold M.R., Leon A.R., Herre J.M., Hood M., Rashtian M., Kremers M., Crozier I., Lee K.L., Smith W., Burke M.C. Safety and efficacy of a totally subcutaneous implantable-cardioverter defibrillator. Circulation. 2013;128(9):944–953. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

