A protocol to investigate cellular and circuit mechanisms generating sharp wave ripple oscillations in rodent basolateral amygdala using ex vivo slices
- PMID: 35072114
- PMCID: PMC8761775
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2021.101085
A protocol to investigate cellular and circuit mechanisms generating sharp wave ripple oscillations in rodent basolateral amygdala using ex vivo slices
Abstract
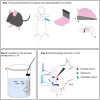
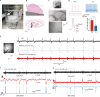
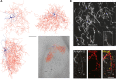
Basolateral amygdala circuits generate oscillatory network activity to process and remember emotion-tagged events. Ex vivo preparations that recapitulate network activities seen in vivo provide an ideal system to investigate the mechanisms driving these network oscillations. Here we describe an ex vivo preparation of basolateral amygdala slices from rodents for measuring the generated sharp wave ripple oscillations (SWs) using local field potential recording and targeted recording from chandelier neurons that initiate SWs. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Perumal et al. (2021).
Keywords: Cell Biology; Cognitive Neuroscience; Model Organisms; Neuroscience.
© 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Microcircuit mechanisms for the generation of sharp-wave ripples in the basolateral amygdala: A role for chandelier interneurons.Cell Rep. 2021 May 11;35(6):109106. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109106. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 33979609 Free PMC article.
-
A protocol to investigate neural coupling of brain oscillations in rodents using in vivo electrophysiological recordings.STAR Protoc. 2023 Sep 15;4(3):102414. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2023.102414. Epub 2023 Jul 11. STAR Protoc. 2023. PMID: 37436903 Free PMC article.
-
Impairment of Sharp-Wave Ripples in a Murine Model of Dravet Syndrome.J Neurosci. 2019 Nov 13;39(46):9251-9260. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0890-19.2019. Epub 2019 Sep 19. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31537705 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory Circuits in the Basolateral Amygdala in Aversive Learning and Memory.Front Neural Circuits. 2021 Apr 30;15:633235. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2021.633235. eCollection 2021. Front Neural Circuits. 2021. PMID: 33994955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Structure to Behavior in Basolateral Amygdala-Hippocampus Circuits.Front Neural Circuits. 2017 Oct 31;11:86. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2017.00086. eCollection 2017. Front Neural Circuits. 2017. PMID: 29163066 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential Regulation of Prelimbic and Thalamic Transmission to the Basolateral Amygdala by Acetylcholine Receptors.J Neurosci. 2023 Feb 1;43(5):722-735. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2545-21.2022. Epub 2022 Dec 19. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36535767 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct mechanisms of allopregnanolone and diazepam underlie neuronal oscillations and differential antidepressant effect.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Jan 8;17:1274459. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1274459. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38259500 Free PMC article.
-
Trauma in Neonatal Acute Brain Slices Alters Calcium and Network Dynamics and Causes Calpain-Mediated Cell Death.eNeuro. 2024 Jul 8;11(7):ENEURO.0007-24.2024. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0007-24.2024. Print 2024 Jul. eNeuro. 2024. PMID: 38886064 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pare D., Collins D.R., Pelletier J.G. Amygdala oscillations and the consolidation of emotional memories. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2002;6:306–314. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

