TP53 mutation defines a unique subgroup within complex karyotype de novo and therapy-related MDS/AML
- PMID: 35073573
- PMCID: PMC9092405
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021006239
TP53 mutation defines a unique subgroup within complex karyotype de novo and therapy-related MDS/AML
Abstract
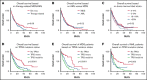
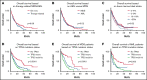
A subset of myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) show complex karyotype (CK), and these cases include a relatively high proportion of cases of therapy-related myeloid neoplasms and TP53 mutations. We aimed to evaluate the clinicopathologic features of outcome of 299 AML and MDS patients with CK collected from multiple academic institutions. Mutations were present in 287 patients (96%), and the most common mutation detected was in TP53 gene (247, 83%). A higher frequency of TP53 mutations was present in therapy-related cases (P = .008), with a trend for worse overall survival (OS) in therapy-related patients as compared with de novo disease (P = .08) and within the therapy-related group; the presence of TP53 mutation strongly predicted for worse outcome (P = .0017). However, there was no difference in survival between CK patients based on categorization of AML vs MDS (P = .96) or presence of absence of circulating blasts ≥1% (P = .52). TP53-mutated patients presented with older age (P = .06) and lower hemoglobin levels (P = .004) and marrow blast counts (P = .02) compared with those with CK lacking TP53 mutation. Multivariable analysis identified presence of multihit TP53 mutation as strongest predictor of worse outcome, whereas neither a diagnosis of AML vs MDS nor therapy-relatedness independently influenced OS. Our findings suggest that among patients with MDS and AML, the presence of TP53 mutation (in particular multihit TP53 mutation) in the context of CK identifies a homogeneously aggressive disease, irrespective of the blast count at presentation or therapy-relatedness. The current classification of these cases into different disease categories artificially separates a single biologic disease entity.
© 2022 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Haase D, Germing U, Schanz J, et al. . New insights into the prognostic impact of the karyotype in MDS and correlation with subtypes: evidence from a core dataset of 2124 patients. Blood. 2007;110(13):4385-4395. - PubMed
-
- Trost D, Hildebrandt B, Beier M, Müller N, Germing U, Royer-Pokora B. Molecular cytogenetic profiling of complex karyotypes in primary myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2006;165(1):51-63. - PubMed
-
- Germing U, Strupp C, Kuendgen A, et al. . Prospective validation of the WHO proposals for the classification of myelodysplastic syndromes. Haematologica. 2006;91(12):1596-1604. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

