Monocyte miRNAs Are Associated With Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 35073575
- PMCID: PMC8965663
- DOI: 10.2337/db21-0704
Monocyte miRNAs Are Associated With Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
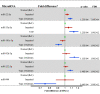
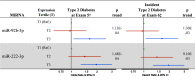
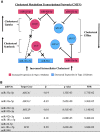
miRNAs are small noncoding RNAs that may contribute to common diseases through epigenetic regulation of gene expression. Little is known regarding the role of miRNAs in type 2 diabetes (T2D). We performed miRNA sequencing and transcriptomic profiling of peripheral monocytes from the longitudinal Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) (N = 1,154). We examined associations between miRNAs and prevalent impaired fasting glucose and T2D and evaluated the T2D-associated miRNA effect on incident T2D. Of 774 detected miRNAs, 6 (miR-22-3p, miR-33a-5p, miR-181c-5p, miR-92b-3p, miR-222-3p, and miR-944) were associated with prevalent T2D. For five of the six miRNAs (all but miR-222-3p), our findings suggest a dose-response relationship with impaired fasting glucose and T2D. Two of the six miRNAs were associated with incident T2D (miR-92b-3p: hazard ratio [HR] 1.64, P = 1.30E-03; miR-222-3p: HR 1.97, P = 9.10E-03) in the highest versus lowest tertile of expression. Most of the T2D-associated miRNAs were also associated with HDL cholesterol concentrations. The genes targeted by these miRNAs belong to key nodes of a cholesterol metabolism transcriptomic network. Higher levels of miRNA expression expected to increase intracellular cholesterol accumulation in monocytes are linked to an increase in T2D risk.
© 2022 by the American Diabetes Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- De Rosa S, Curcio A, Indolfi C. Emerging role of microRNAs in cardiovascular diseases. Circ J 2014;78:567–575 - PubMed
-
- Wendt A, Esguerra JL, Eliasson L. Islet microRNAs in health and type-2 diabetes. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2018;43:46–52 - PubMed
-
- Esguerra JLS, Nagao M, Ofori JK, Wendt A, Eliasson L. MicroRNAs in islet hormone secretion. Diabetes Obes Metab 2018;20(Suppl. 2):11–19 - PubMed
-
- Chen K, Rajewsky N. The evolution of gene regulation by transcription factors and microRNAs. Nat Rev Genet 2007;8:93–103 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01 HC095168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL135009/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL119962/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00002/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00005/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK101921/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00001/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL101250/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00003/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001420/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00004/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00007/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG054474/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL126477/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00006/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001881/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK103531/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

