The role and therapeutic potential of stem cells in skeletal muscle in sarcopenia
- PMID: 35073997
- PMCID: PMC8785537
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-022-02706-5
The role and therapeutic potential of stem cells in skeletal muscle in sarcopenia
Abstract
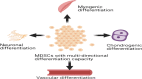
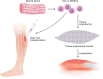
Sarcopenia is a common age-related skeletal muscle disorder featuring the loss of muscle mass and function. In regard to tissue repair in the human body, scientists always consider the use of stem cells. In skeletal muscle, satellite cells (SCs) are adult stem cells that maintain tissue homeostasis and repair damaged regions after injury to preserve skeletal muscle integrity. Muscle-derived stem cells (MDSCs) and SCs are the two most commonly studied stem cell populations from skeletal muscle. To date, considerable progress has been achieved in understanding the complex associations between stem cells in muscle and the occurrence and treatment of sarcopenia. In this review, we first give brief introductions to sarcopenia, SCs and MDSCs. Then, we attempt to untangle the differences and connections between these two types of stem cells and further elaborate on the interactions between sarcopenia and stem cells. Finally, our perspectives on the possible application of stem cells for the treatment of sarcopenia in future are presented. Several studies emerging in recent years have shown that changes in the number and function of stem cells can trigger sarcopenia, which in turn leads to adverse influences on stem cells because of the altered internal environment in muscle. A better understanding of the role of stem cells in muscle, especially SCs and MDSCs, in sarcopenia will facilitate the realization of novel therapy approaches based on stem cells to combat sarcopenia.
Keywords: Muscle stem cells; Muscle-derived stem cells; Sarcopenia; Satellite cells.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regenerative decline of stem cells in sarcopenia.Mol Aspects Med. 2016 Aug;50:109-17. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2016.02.002. Epub 2016 Feb 24. Mol Aspects Med. 2016. PMID: 26921790 Review.
-
Thyroid Hormone Receptor Alpha is Essential to Maintain the Satellite Cell Niche During Skeletal Muscle Injury and Sarcopenia of Aging.Thyroid. 2017 Oct;27(10):1316-1322. doi: 10.1089/thy.2017.0021. Thyroid. 2017. PMID: 28847239 Free PMC article.
-
Restoring Mitochondrial Function and Muscle Satellite Cell Signaling: Remedies against Age-Related Sarcopenia.Biomolecules. 2024 Mar 28;14(4):415. doi: 10.3390/biom14040415. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38672432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of Skeletal Muscle Atrophy and Molecular Circuitry of Stem Cell Fate in Skeletal Muscle Regeneration and Aging.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2023 Jun 16;78(Suppl 1):14-18. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glad023. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37325966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Skeletal Muscle Stem Cells and the Microenvironment Regulation in Sarcopenia:A Review.Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2024 Dec;46(6):958-964. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.16114. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 39773515 Review.
Cited by
-
Decrease in the expression of muscle-specific miRNAs, miR-133a and miR-1, in myoblasts with replicative senescence.PLoS One. 2023 Jan 17;18(1):e0280527. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0280527. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36649291 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Amino Acids and Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Arginine Transporter SLC7A2 Is a Novel Regulator of Myogenic Differentiation.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 20;25(1):95. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010095. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203268 Free PMC article.
-
Chimeric Cell Therapies as a Novel Approach for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) and Muscle Regeneration.Biomolecules. 2024 May 13;14(5):575. doi: 10.3390/biom14050575. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38785982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Therapeutic Strategies in Sarcopenia: An Updated Review on Pathogenesis and Treatment Advances.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 12;25(8):4300. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084300. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38673885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD9, a novel potential biomarker of sarcopenia.Sci Rep. 2025 May 30;15(1):19099. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-04331-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40447842 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources