SARS-CoV-2 NSP5 and N protein counteract the RIG-I signaling pathway by suppressing the formation of stress granules
- PMID: 35075101
- PMCID: PMC8785035
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-022-00878-3
SARS-CoV-2 NSP5 and N protein counteract the RIG-I signaling pathway by suppressing the formation of stress granules
Abstract
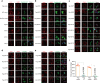
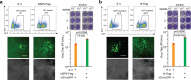
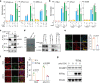
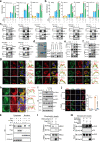
As a highly pathogenic human coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2 has to counteract an intricate network of antiviral host responses to establish infection and spread. The nucleic acid-induced stress response is an essential component of antiviral defense and is closely related to antiviral innate immunity. However, whether SARS-CoV-2 regulates the stress response pathway to achieve immune evasion remains elusive. In this study, SARS-CoV-2 NSP5 and N protein were found to attenuate antiviral stress granule (avSG) formation. Moreover, NSP5 and N suppressed IFN expression induced by infection of Sendai virus or transfection of a synthetic mimic of dsRNA, poly (I:C), inhibiting TBK1 and IRF3 phosphorylation, and restraining the nuclear translocalization of IRF3. Furthermore, HEK293T cells with ectopic expression of NSP5 or N protein were less resistant to vesicular stomatitis virus infection. Mechanistically, NSP5 suppressed avSG formation and disrupted RIG-I-MAVS complex to attenuate the RIG-I-mediated antiviral immunity. In contrast to the multiple targets of NSP5, the N protein specifically targeted cofactors upstream of RIG-I. The N protein interacted with G3BP1 to prevent avSG formation and to keep the cofactors G3BP1 and PACT from activating RIG-I. Additionally, the N protein also affected the recognition of dsRNA by RIG-I. This study revealed the intimate correlation between SARS-CoV-2, the stress response, and innate antiviral immunity, shedding light on the pathogenic mechanism of COVID-19.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82101856/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81901604/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81930039/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 31730026/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81525012/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

