Transcription shifts in gut bacteria shared between mothers and their infants
- PMID: 35075183
- PMCID: PMC8786960
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-04848-1
Transcription shifts in gut bacteria shared between mothers and their infants
Abstract
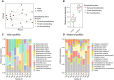
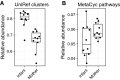
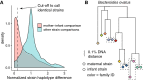
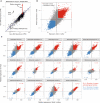
The infant gut microbiome contains a portion of bacteria that originate from the maternal gut. In the infant gut these bacteria encounter a new metabolic environment that differs from the adult gut, consequently requiring adjustments in their activities. We used pilot community RNA sequencing data (metatranscriptomes) from ten mother-infant dyads participating in the NiPPeR Study to characterize bacterial gene expression shifts following mother-to-infant transmission. Maternally-derived bacterial strains exhibited large scale gene expression shifts following the transmission to the infant gut, with 12,564 activated and 14,844 deactivated gene families. The implicated genes were most numerous and the magnitude shifts greatest in Bacteroides spp. This pilot study demonstrates environment-dependent, strain-specific shifts in gut bacteria function and underscores the importance of metatranscriptomic analysis in microbiome studies.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
OS and SC are employees of Société des Produits Nestlé (SPN). KMG has received reimbursement for speaking at conferences sponsored by companies selling nutritional products, and is part of an academic consortium that has received research funding from Abbott Nutrition, Nestec, BenevolentAI Bio Ltd. and Danone. TV, BW, SYC, WSC and JOS declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

