Effects of a physical activity intervention on schoolchildren fitness
- PMID: 35075816
- PMCID: PMC8787616
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.15115
Effects of a physical activity intervention on schoolchildren fitness
Abstract
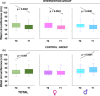
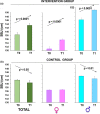
The global prevalence of childhood obesity is high. Obesity main causes are linked to sedentary lifestyles. Increasing physical activity (PA) and reducing sedentary activities are recommended to prevent and treat obesity. This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of a 6-month school PA intervention on obesity prevention and healthy behaviors in school-aged children. Participating students (10-11 years of age) were randomly divided into an intervention group and a control group. Children in the intervention group (n = 80) participated in a multicomponent PA that included improvement in extracurricular physical activities (with an additional 40 min per day for 5/6 days per week). Children (n = 80) in the control group participated in usual practice. Participants had mean body mass index of 19.7 ± 2.9 kg/m2 , and 33.7% of them were overweight or with obesity at T0. The change in body mass index in intervention group (-2.4 ± 0.6 kg/m2 ) was significantly different from that in control group (3.01 ± 1.8 kg/m2 ). The effects on waist circumference, waist-to-height ratio, and physic fitness were also significant in intervention group compared with control group (all p < 0.05). Furthermore, there is a significant decrease in overweight or children with obesity in the experimental group (to 17.5%, p < 0.05). These findings suggest that a school-based intervention program represents an effective strategy for decreasing the number of overweight and children with obesity.
Keywords: BMI; children obesity; overweight; physical activity; waist circumference.
© 2022 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest and they have ethics approval and consent to participate.
Figures




References
-
- Abarca‐Gómez, L. , Abdeen, Z. A. , Hamid, Z. A. , Abu‐Rmeileh, N. M. , Acosta‐Cazares, B. , Acuin, C. , Adams, R. J. , Aekplakorn, W. , Afsana, K. , Aguilar‐Salinas, C. A. , Agyemang, C. , Ahmadvand, A. , Ahrens, W. , Ajlouni, K. , Akhtaeva, N. , Al‐Hazzaa, H. M. , Al‐Othman, A. R. , Al‐Raddadi, R. , Al Buhairan, F. , … Ezzati, M. ; NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD‐RisC) . (2017). Worldwide trends in body‐mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 2416 population‐based measurement studies in 128.9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet, 390(10113), 2627–2642. 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32129-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Afshin, A. , Forouzanfar, M. H. , Reitsma, M. B. , Sur, P. , Estep, K. , Lee, A. , Marczak, L. , Mokdad, A. H. , Moradi‐Lakeh, M. , Naghavi, M. , Salama, J. S. , Vos, T. , Abate, K. H. , Abbafati, C. , Ahmed, M. B. , Al‐Aly, Z. , Alkerwi, A. , Al‐Raddadi, R. , Amare, A. T. , … Murray, C. J. L. (2017). Health effects of overweight and obesity in 195 countries over 25 years. New England Journal of Medicine, 377(1), 13–27. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Battaglia, G. , Giustino, V. , Tabacchi, G. , Lanza, M. , Schena, F. , Biino, V. , Giuriato, M. , Gallotta, M. C. , Guidetti, L. , Baldari, C. , Gennaro, A. , Palma, A. , & Bellafiore, M. (2021). Interrelationship between age, gender, and weight status on motor coordination in Italian children and early adolescents aged 6–13 years old. Frontiers in Pediatrics, 9, 965. 10.3389/fped.2021.738294 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

