Mapping the complex causal mechanisms of drinking and driving behaviors among adolescents and young adults
- PMID: 35078103
- PMCID: PMC8925313
- DOI: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2022.114732
Mapping the complex causal mechanisms of drinking and driving behaviors among adolescents and young adults
Abstract
Background: The proportion of motor vehicle crash fatalities involving alcohol-impaired drivers declined substantially between 1982 and 1997, but progress stopped after 1997. The systemic complexity of alcohol-impaired driving contributes to the persistence of this problem. This study aims to identify and map key feedback mechanisms that affect alcohol-impaired driving among adolescents and young adults in the U.S.
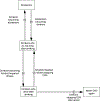
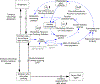
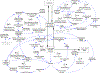
Methods: We apply the system dynamics approach to the problem of alcohol-impaired driving and bring a feedback perspective for understanding drivers and inhibitors of the problem. The causal loop diagram (i.e., map of dynamic hypotheses about the structure of the system producing observed behaviors over time) developed in this study is based on the output of two group model building sessions conducted with multidisciplinary subject-matter experts bolstered with extensive literature review.
Results: The causal loop diagram depicts diverse influences on youth impaired driving including parents, peers, policies, law enforcement, and the alcohol industry. Embedded in these feedback loops are the physical flow of youth between the categories of abstainers, drinkers who do not drive after drinking, and drinkers who drive after drinking. We identify key inertial factors, discuss how delay and feedback processes affect observed behaviors over time, and suggest strategies to reduce youth impaired driving.
Conclusion: This review presents the first causal loop diagram of alcohol-impaired driving among adolescents and it is a vital first step toward quantitative simulation modeling of the problem. Through continued research, this model could provide a powerful tool for understanding the systemic complexity of impaired driving among adolescents, and identifying effective prevention practices and policies to reduce youth impaired driving.
Keywords: Alcohol; Health policies; Parental monitoring; Peers; System dynamics; Youth drinking and driving.
Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest disclosure:
The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to this article to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- ANDERSEN D & RICHARDSON G 1997. Scripts for group model building. System Dynamics Review, 13, 107–129.
-
- ANDERSEN D, VENNIX J, RICHARDSON G & ROUWETTE EAJA 2007. Group Model Building: Problem Structing, Policy Simulation and Decision Support. The Journal of the Operational Research Society, 58, 691–694.
-
- BOGGS MM 2017. The impact of exposure to alcohol advertisements on adolescents: A literature review. International Public Health Journal, 9, 13.
-
- BORSARI B & CAREY KB 2001. Peer influences on college drinking: A review of the research. Journal of substance abuse, 13, 391–424. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

