Characterization of the COPD alveolar niche using single-cell RNA sequencing
- PMID: 35078977
- PMCID: PMC8789871
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-28062-9
Characterization of the COPD alveolar niche using single-cell RNA sequencing
Abstract
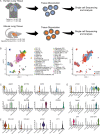
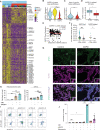
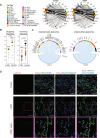
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a leading cause of death worldwide, however our understanding of cell specific mechanisms underlying COPD pathobiology remains incomplete. Here, we analyze single-cell RNA sequencing profiles of explanted lung tissue from subjects with advanced COPD or control lungs, and we validate findings using single-cell RNA sequencing of lungs from mice exposed to 10 months of cigarette smoke, RNA sequencing of isolated human alveolar epithelial cells, functional in vitro models, and in situ hybridization and immunostaining of human lung tissue samples. We identify a subpopulation of alveolar epithelial type II cells with transcriptional evidence for aberrant cellular metabolism and reduced cellular stress tolerance in COPD. Using transcriptomic network analyses, we predict capillary endothelial cells are inflamed in COPD, particularly through increased CXCL-motif chemokine signaling. Finally, we detect a high-metallothionein expressing macrophage subpopulation enriched in advanced COPD. Collectively, these findings highlight cell-specific mechanisms involved in the pathobiology of advanced COPD.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
N.K. reports personal fees from Biogen Idec, Boehringer Ingelheim, Third Rock, Samumed, Numedii, Astra Zeneca, Life Max, Tervnce, RohBar, and Pliant. Equity in Pliant. Collaboration with Miragen, Astra Zeneca. Grant from Veracyte, all outside the submitted work; In addition, N.K. has a patent New Therapies in Pulmonary Fibrosis, and a patent for Peripheral Blood Gene Expression licensed to Biotech. L.E.N. reports grants from Humacyte Inc., outside the submitted work. E.A.A. and S.G.C. report personal fees from Novartis Institutes of BioMedical Research, outside the submitted work. K.H.J. and P.N.T. are employed by Intomics. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 HL127349/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 HL154275/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG021342/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL138540/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL155948/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- J 4547/FWF_/Austrian Science Fund FWF/Austria
- R01 HL153604/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL141852/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL135402/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 TR002445/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL152953/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F30 HL143906/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL145567/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL114501/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

