A fuzzy-enhanced deep learning approach for early detection of Covid-19 pneumonia from portable chest X-ray images
- PMID: 35079203
- PMCID: PMC8776345
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neucom.2022.01.055
A fuzzy-enhanced deep learning approach for early detection of Covid-19 pneumonia from portable chest X-ray images
Abstract
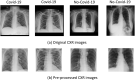
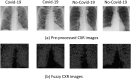
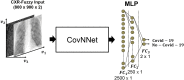
The Covid-19 pandemic is the defining global health crisis of our time. Chest X-Rays (CXR) have been an important imaging modality for assisting in the diagnosis and management of hospitalised Covid-19 patients. However, their interpretation is time intensive for radiologists. Accurate computer aided systems can facilitate early diagnosis of Covid-19 and effective triaging. In this paper, we propose a fuzzy logic based deep learning (DL) approach to differentiate between CXR images of patients with Covid-19 pneumonia and with interstitial pneumonias not related to Covid-19. The developed model here, referred to as CovNNet, is used to extract some relevant features from CXR images, combined with fuzzy images generated by a fuzzy edge detection algorithm. Experimental results show that using a combination of CXR and fuzzy features, within a deep learning approach by developing a deep network inputed to a Multilayer Perceptron (MLP), results in a higher classification performance (accuracy rate up to 81%), compared to benchmark deep learning approaches. The approach has been validated through additional datasets which are continously generated due to the spread of the virus and would help triage patients in acute settings. A permutation analysis is carried out, and a simple occlusion methodology for explaining decisions is also proposed. The proposed pipeline can be easily embedded into present clinical decision support systems.
Keywords: Chest X-ray; Convolutional Neural Network; Covid-19; Fuzzy logic; Portable systems; explainable Artificial Intelligence.
© 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





References
-
- Covid-19 dashboard by the center for systems science and engineering (csse) at johns hopkins university (jhu). https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html, accessed: 2021-10-15.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
