Genetic Characteristics of Mismatch Repair-deficient Glioblastoma
- PMID: 35079518
- PMCID: PMC8769403
- DOI: 10.2176/nmccrj.cr.2020-0366
Genetic Characteristics of Mismatch Repair-deficient Glioblastoma
Abstract
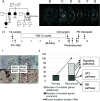
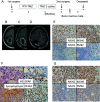
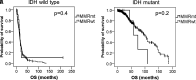
Mismatch repair (MMR) gene deficiency is rarely observed in gliomas, a constitutional defect is associated with tumorigenesis in Lynch syndrome, and an acquired defect is associated with hypermutation after temozolomide treatment. However, the meaning of MMR gene deficiency in gliomas is unclear. Two cases of MMR-deficient glioblastomas are reported, and mutational status of oncogenes was compared between primary and recurrent tumor samples in a glioblastoma patient with Lynch syndrome. Additionally, the characteristics of MMR-deficient glioblastomas were analyzed using public glioma datasets to determine the meaning of MMR deficiency in gliomas. Case 1 was a glioblastoma patient with Lynch syndrome, and treatment with pembrolizumab for the recurrent tumor was temporarily effective for a short period. Comparison of mutational changes between primary and recurrent tumor samples showed many additional mutated genes associated with multiple signaling pathways in the recurrent tumor. Tumor recurrence and chemoresistance could be associated with intratumoral heterogeneity and accelerated tumor progression due to defects of multiple signaling pathways. Case 2 was a glioblastoma patient with acquired MMR gene deficiency, and she died of rapid progression of bone marrow metastases. This rare clinical course was considered to be associated with gene expression changes and heterogeneity that resulted from MMR gene deficiency. Two cases of MMR gene-deficient glioblastomas were presented, and their genetic characteristics suggested that their clinical courses could be associated with MMR gene deficiency.
Keywords: Lynch syndrome; bone marrow; glioma; mismatch repair; pembrolizumab.
© 2021 The Japan Neurosurgical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest Disclosure The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
