Systemic administration of dendrimer N-acetyl cysteine improves outcomes and survival following cardiac arrest
- PMID: 35079634
- PMCID: PMC8780014
- DOI: 10.1002/btm2.10259
Systemic administration of dendrimer N-acetyl cysteine improves outcomes and survival following cardiac arrest
Abstract
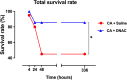
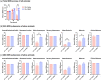
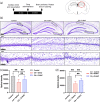
Cardiac arrest (CA), the sudden cessation of effective cardiac pumping function, is still a major clinical problem with a high rate of early and long-term mortality. Post-cardiac arrest syndrome (PCAS) may be related to an early systemic inflammatory response leading to exaggerated and sustained neuroinflammation. Therefore, early intervention with targeted drug delivery to attenuate neuroinflammation may greatly improve therapeutic outcomes. Using a clinically relevant asphyxia CA model, we demonstrate that a single (i.p.) dose of dendrimer-N-acetylcysteine conjugate (D-NAC), can target "activated" microglial cells following CA, leading to an improvement in post-CA survival rate compared to saline (86% vs. 45%). D-NAC treatment also significantly improved gross neurological score within 4 h of treatment (p < 0.05) and continued to show improvement at 48 h (p < 0.05). Specifically, there was a substantial impairment in motor responses after CA, which was subsequently improved with D-NAC treatment (p < 0.05). D-NAC also mitigated hippocampal cell density loss seen post-CA in the CA1 and CA3 subregions (p < 0.001). These results demonstrate that early therapeutic intervention even with a single D-NAC bolus results in a robust sustainable improvement in long-term survival, short-term motor deficits, and neurological recovery. Our current work lays the groundwork for a clinically relevant therapeutic approach to treating post-CA syndrome.
Keywords: N‐acetyl cysteine; cardiac arrest; dendrimer; inflammation; rat.
© 2021 The Authors. Bioengineering & Translational Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Institute of Chemical Engineers.
Conflict of interest statement
Rangaramanujam M. Kannan, Sujatha Kannan, and Rishi Sharma have awarded and pending patents relating to the D‐NAC and dendrimer platform. Rangaramanujam M. Kannan and Sujatha Kannan are co‐founders and have financial interests in Ashvattha Therapeutics Inc., a startup involved with the translation of dendrimer drug delivery platforms.
Figures


References
-
- Atwood C, Eisenberg MS, Herlitz J, Rea TD. Incidence of EMS‐treated out‐of‐hospital cardiac arrest in Europe. Resuscitation. 2005;67(1):75‐80. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin EJ, Virani SS, Callaway CW, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2018 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2018;137(12):e67‐e492. - PubMed
-
- Sans S, Kesteloot H, Do Kromhout, Force T. The burden of cardiovascular diseases mortality in Europe: task force of the European society of cardiology on cardiovascular mortality and morbidity statistics in. Paper presented at: Europe' European Heart Journal; 1997. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

