Recent advances and clinical application in point-of-care testing of SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 35080017
- PMCID: PMC9015580
- DOI: 10.1002/jmv.27617
Recent advances and clinical application in point-of-care testing of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
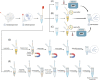
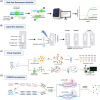
The novel coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) caused by SARS-CoV-2 spread rapidly worldwide, posing a severe threat to public life and health. It is significant to realize rapid testing and timely control of epidemic situations under the condition of limited resources. However, laboratory-based standardized nucleic acid detection methods have a long turnaround time and high cost, so it is urgent to develop convenient methods for detecting COVID-19. This paper summarizes the point-of-care testing (POCT) developed for novel coronavirus from three aspects: nucleic acid extraction, nucleic acid amplification, and detection methods. This paper introduces a commercial real-time detection system that integrates the abovementioned three steps and the matters needing attention in use. The primary purpose of this review is to provide a reference for emergency response and rapid deployment of COVID-19 and some other emerging infectious diseases.
Keywords: COVID-19; instant detection; novel coronavirus; nucleic acid detection.
© 2022 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Based on Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (NAATs) and Its Integration into Nanomedicine and Microfluidic Devices as Point-of-Care Testing (POCT).Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 16;24(12):10233. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210233. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sequence-specific and multiplex detection of COVID-19 virus (SARS-CoV-2) using proofreading enzyme-mediated probe cleavage coupled with isothermal amplification.Biosens Bioelectron. 2021 Apr 15;178:113041. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113041. Epub 2021 Jan 28. Biosens Bioelectron. 2021. PMID: 33545551 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in nucleic acid amplification techniques (NAATs): COVID-19 point-of-care diagnostics as an example.Biosens Bioelectron. 2022 Jun 15;206:114109. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2022.114109. Epub 2022 Feb 26. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022. PMID: 35245867 Review.
-
Application experience of a rapid nucleic acid detection system for COVID-19.Microbes Infect. 2022 Jun;24(4):104945. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2022.104945. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Microbes Infect. 2022. PMID: 35093551 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Visby medical COVID-19 point of care nucleic acid amplification test.Clin Biochem. 2023 Jul;117:1-3. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2021.11.007. Epub 2021 Nov 17. Clin Biochem. 2023. PMID: 34798145 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2 variants: Impact on biological and clinical outcome.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 10;9:995960. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.995960. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36438034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Performance and application evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 antigen assay.J Med Virol. 2022 Aug;94(8):3548-3553. doi: 10.1002/jmv.27798. Epub 2022 Apr 30. J Med Virol. 2022. PMID: 35445404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Critical Review on the Sensing, Control, and Manipulation of Single Molecules on Optofluidic Devices.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 Jun 18;13(6):968. doi: 10.3390/mi13060968. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35744582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fluorescence origami paper-based analytical device based on strand displacement assay for SARS-CoV-2 cDNA detection.Mikrochim Acta. 2025 May 28;192(6):381. doi: 10.1007/s00604-025-07228-4. Mikrochim Acta. 2025. PMID: 40434444
-
Point-of-care testing in companion and food animal disease diagnostics.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Nov 25;9:1056440. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.1056440. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36504865 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zachariah R, Harries AD. The WHO clinical case definition for suspected cases of Ebola virus disease arriving at Ebola holding units: reason to worry? Lancet Infect Dis. 2015;15(9):989‐990. - PubMed
-
- Li TG, Wang M. [Be alert to superposed effect of seasonal influenza while fighting against novel coronavirus pneumonia]. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020;54(0):E002. - PubMed
-
- Florkowski C, Don‐Wauchope A, Gimenez N, Rodriguez‐Capote K, Wils J, Zemlin A. Point‐of‐care testing (POCT) and evidence‐based laboratory medicine (EBLM)—does it leverage any advantage in clinical decision making? Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2017;54(7‐8):471‐494. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Key Project of Provincial Ministry Coconstruction, Health Science and Technology Project Plan of Zhejiang Province: WKJ-ZJ-2128
- Key Laboratory of Women's Reproductive Health Research of Zhejiang Province: ZDFY2020-RH-0006)
- The National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant/Award Numbers: U20A20351) and Key Research and Development Plan of Zhejiang Province (Grant/Award Numbers: 2021C03079)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

