From cultivar mixtures to allelic mixtures: opposite effects of allelic richness between genotypes and genotype richness in wheat
- PMID: 35081666
- PMCID: PMC9306887
- DOI: 10.1111/nph.17915
From cultivar mixtures to allelic mixtures: opposite effects of allelic richness between genotypes and genotype richness in wheat
Abstract
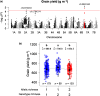
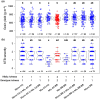
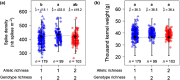
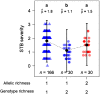
Agroecosystem diversification through increased crop genetic diversity could provide multiple services such as improved disease control or increased productivity. However, we still poorly understand how genetic diversity affects agronomic performance. We grew 179 inbred lines of durum wheat in pure stands and in 202 binary mixtures in field conditions. We then tested the effect of allelic richness between genotypes and genotype richness on grain yield and Septoria tritici blotch disease. Allelic richness was tested at 19K single nucleotide polymorphisms distributed along the durum wheat genome. Both genotype richness and allelic richness could be equal to 1 or 2. Mixtures were overall more productive and less diseased than their pure stand components. Yet, we identified one locus at which allelic richness between genotypes was associated with increased disease severity and decreased grain yield. The effect of allelic richness at this locus was stronger than the effect of genotype richness on grain yield (-7.6% vs +5.7%). Our results suggest that positive effects of crop diversity can be reversed by unfavourable allelic associations. This highlights the need to integrate genomic data into crop diversification strategies. More generally, investigating plant-plant interactions at the genomic level is promising to better understand biodiversity-ecosystem functioning relationships.
Keywords: Septoria tritici blotch; allelic richness; crop; diversity; genome-wide analysis; plant-plant interactions; varietal mixtures.
© 2022 The Authors. New Phytologist © 2022 New Phytologist Foundation.
Figures


References
-
- Altieri MA. 1999. The ecological role of biodiversity in agroecosystems. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 74: 19–31.
-
- Ballini E, Tavaud M, Ducasse A, Sanchez D, Paux E, Kitt J, Charmet G, Audigeos D, Roumet P, David J et al. 2020. Genome wide association mapping for resistance to multiple fungal pathogens in a panel issued from a broad composite cross‐population of tetraploid wheat Triticum turgidum . Euphytica 216: 92.
-
- Barot S, Allard V, Cantarel A, Enjalbert J, Gauffreteau A, Goldringer I, Lata J‐C, Roux XL, Niboyet A, Porcher E. 2017. Designing mixtures of varieties for multifunctional agriculture with the help of ecology. A review. Agronomy for Sustainable Development 37: 13.
-
- Borg J, Kiær LP, Lecarpentier C, Goldringer I, Gauffreteau A, Saint‐Jean S, Barot S, Enjalbert J. 2018. Unfolding the potential of wheat cultivar mixtures: a meta‐analysis perspective and identification of knowledge gaps. Field Crops Research 221: 298–313.
-
- Castro AC, Simón MR. 2016. Effect of tolerance to Septoria tritici blotch on grain yield, yield components and grain quality in Argentinean wheat cultivars. Crop Protection 90: 66–76.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

