Structural and mechanistic basis of reiterative transcription initiation
- PMID: 35082149
- PMCID: PMC8812562
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2115746119
Structural and mechanistic basis of reiterative transcription initiation
Abstract
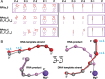
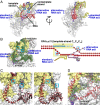
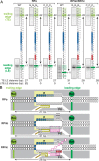
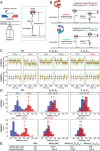
Reiterative transcription initiation, observed at promoters that contain homopolymeric sequences at the transcription start site, generates RNA products having 5' sequences noncomplementary to the DNA template. Here, using crystallography and cryoelectron microscopy to define structures, protein-DNA photocrosslinking to map positions of RNAP leading and trailing edges relative to DNA, and single-molecule DNA nanomanipulation to assess RNA polymerase (RNAP)-dependent DNA unwinding, we show that RNA extension in reiterative transcription initiation 1) occurs without DNA scrunching; 2) involves a short, 2- to 3-bp, RNA-DNA hybrid; and 3) generates RNA that exits RNAP through the portal by which scrunched nontemplate-strand DNA exits RNAP in standard transcription initiation. The results establish that, whereas RNA extension in standard transcription initiation proceeds through a scrunching mechanism, RNA extension in reiterative transcription initiation proceeds through a slippage mechanism, with slipping of RNA relative to DNA within a short RNA-DNA hybrid, and with extrusion of RNA from RNAP through an alternative RNA exit.
Keywords: DNA scrunching; RNA polymerase; reiterative transcription initiation; transcription; transcriptional slippage.
Copyright © 2022 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


References
-
- Winkelman J. T., Nickels B. E., Ebright R. H., “The transition from transcription initiation to transcription elongation: Start-site selection, initial transcription, and promoter escape” in RNA Polymerase as a Molecular Motor, Landick R., Wang J., Strick T. R., Eds. (RSC Publishing, Cambridge, UK, ed. 2, 2021), pp. 1–24.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

