Costs and Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients With NMO Spectrum Disorders and MOG-Antibody-Associated Disease: CHANCENMO Study
- PMID: 35082170
- PMCID: PMC8935443
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000200052
Costs and Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients With NMO Spectrum Disorders and MOG-Antibody-Associated Disease: CHANCENMO Study
Abstract
Background and objectives: To evaluate costs and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders (NMOSD) and myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-associated disease (MOGAD).
Methods: In this multicenter cross-sectional study, data on consumption of medical and nonmedical resources and work ability were assessed via patient questionnaires. Costs were analyzed in Euros for 2018 from the societal perspective. HRQoL was captured by the EuroQoL Group 5 Dimension 5 Level Scale (EQ-5D-5L) questionnaire. Clinical data were retrieved from the Neuromyelitis Optica Study Group (NEMOS) database.
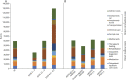
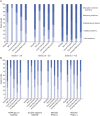
Results: Two hundred twelve patients (80% women, median age 50 [19-83] years, median disease duration 7 [0-43] years, median Expanded Disability Status Scale [EDSS] score 3.5 [0-8.5], 66% aquaporin-4 immunoglobulin G [IgG] positive, 22% MOG IgG positive, 12% double seronegative) were analyzed. The mean total annual per capita cost of illness accounted for €59,574 (95% CI 51,225-68,293 or US dollars [USD] 70,297, 95% CI 60,445-80,586), and the mean index value of the EQ-5D-5L was 0.693 (95% CI 0.65-0.73). The most important cost drivers were informal care costs (28% of total costs), indirect costs (23%), and drugs (16%), especially immunotherapeutics. Costs showed a positive correlation with disease severity (ρ = 0.56, 95% CI 0.45-0.65); in the EDSS score 6.5 to 8.5 subgroup, the mean annual costs were €129,687 (95% CI 101,946-160,336 or USD 153,031, 95% CI 120,296-189,196). The HRQoL revealed a negative correlation to disease severity (ρ = -0.69, 95% CI -0.76 to -0.61); in the EDSS score 6.5 to 8.5 subgroup, the EQ-5D-5L mean index value was 0.195 (95% CI 0.13-0.28). Neither antibody status nor disease duration influenced the total annual costs or HRQoL.
Discussion: These German data from the era without approved preventive immunotherapies show enormous effects of the diseases on costs and quality of life. An early and cost-effective therapy should be provided to prevent long-term disability and to preserve quality of life.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Neurology.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
