Microskeletal stiffness promotes aortic aneurysm by sustaining pathological vascular smooth muscle cell mechanosensation via Piezo1
- PMID: 35082286
- PMCID: PMC8791986
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-27874-5
Microskeletal stiffness promotes aortic aneurysm by sustaining pathological vascular smooth muscle cell mechanosensation via Piezo1
Abstract
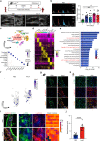
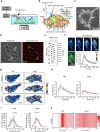
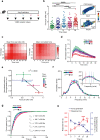
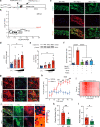
Mechanical overload of the vascular wall is a pathological hallmark of life-threatening abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA). However, how this mechanical stress resonates at the unicellular level of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC) is undefined. Here we show defective mechano-phenotype signatures of VSMC in AAA measured with ultrasound tweezers-based micromechanical system and single-cell RNA sequencing technique. Theoretical modelling predicts that cytoskeleton alterations fuel cell membrane tension of VSMC, thereby modulating their mechanoallostatic responses which are validated by live micromechanical measurements. Mechanistically, VSMC gradually adopt a mechanically solid-like state by upregulating cytoskeleton crosslinker, α-actinin2, in the presence of AAA-promoting signal, Netrin-1, thereby directly powering the activity of mechanosensory ion channel Piezo1. Inhibition of Piezo1 prevents mice from developing AAA by alleviating pathological vascular remodeling. Our findings demonstrate that deviations of mechanosensation behaviors of VSMC is detrimental for AAA and identifies Piezo1 as a novel culprit of mechanically fatigued aorta in AAA.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

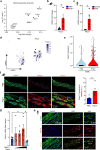
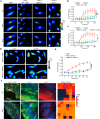
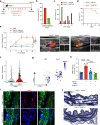
References
-
- Kent KC. Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. New Engl. J. Med. 2014;371:2101–2108. - PubMed
-
- Sampson UK, et al. Estimation of global and regional incidence and prevalence of abdominal aortic aneurysms 1990 to 2010. Glob. Heart. 2014;9:159–170. - PubMed
-
- Raffort J, et al. Monocytes and macrophages in abdominal aortic aneurysm. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2017;14:457–471. - PubMed
-
- Hellenthal FAMVI, Buurman WA, Wodzig WKWH, Schurink GWH. Biomarkers of AAA progression. Part 1: extracellular matrix degeneration. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2009;6:464–474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

