Overexpression of the dystrophins Dp40 and Dp40L170P modifies neurite outgrowth and the protein expression profile of PC12 cells
- PMID: 35082358
- PMCID: PMC8791958
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-05271-2
Overexpression of the dystrophins Dp40 and Dp40L170P modifies neurite outgrowth and the protein expression profile of PC12 cells
Abstract
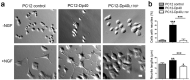
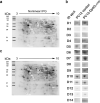
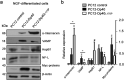
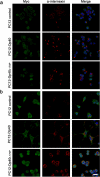
Dp40 is ubiquitously expressed including the central nervous system. In addition to being present in the nucleus, membrane, and cytoplasm, Dp40 is detected in neurites and postsynaptic spines in hippocampal neurons. Although Dp40 is expressed from the same promoter as Dp71, its role in the cognitive impairment present in Duchenne muscular dystrophy patients is still unknown. Here, we studied the effects of overexpression of Dp40 and Dp40L170P during the neuronal differentiation of PC12 Tet-On cells. We found that Dp40 overexpression increased the percentage of PC12 cells with neurites and neurite length, while Dp40L170P overexpression decreased them compared to Dp40 overexpression. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis analysis showed that the protein expression profile was modified in nerve growth factor-differentiated PC12-Dp40L170P cells compared to that of the control cells (PC12 Tet-On). The proteins α-internexin and S100a6, involved in cytoskeletal structure, were upregulated. The expression of vesicle-associated membrane proteins increased in differentiated PC12-Dp40 cells, in contrast to PC12-Dp40L170P cells, while neurofilament light-chain was decreased in both differentiated cells. These results suggest that Dp40 has an important role in the neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells through the regulation of proteins involved in neurofilaments and exocytosis of synaptic vesicles, functions that might be affected in PC12-Dp40L170P.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Tinsley JM, Blake DJ, Davies KE. Apo-dystrophin-3: A 2.2kb transcript from the DMD locus encoding the dystrophin glycoprotein binding site. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1993;2:521–524. - PubMed
-
- Fujimoto T, Itoh K, Yaoi T, Fushiki S. Somatodendritic and excitatory postsynaptic distribution of neuron-type dystrophin isoform, Dp40, in hippocampal neurons. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014;452:79–84. - PubMed
-
- Aragón J, et al. EF-hand domains are involved in the differential cellular distribution of dystrophin Dp40. Neurosci. Lett. 2015;600:115–120. - PubMed
-
- Blake DJ, Weir A, Newey SE, Davies KE. Function and genetics of dystrophin and dystrophin-related proteins in muscle. Physiol. Rev. 2002;82:291–329. - PubMed
-
- Suárez-Sánchez R, et al. Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene product dystrophin Dp71d is dependent on the importin α/β and CRM1 nuclear transporters and microtubule motor dynein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2014;1843:985–1001. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

