Introducing a Removable Orthodontic Appliance and Its Effects on Dental Arch Dimensions
- PMID: 35082465
- PMCID: PMC8754278
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-2023
Introducing a Removable Orthodontic Appliance and Its Effects on Dental Arch Dimensions
Abstract
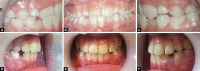
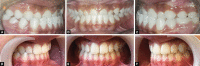
Introduction: Guiding anterior crossbite to a normal position is one of the most important responsibilities of a pediatric dentist or orthodontist to gain both esthetic and function. Crossbite with dental etiology can be treated by a variety of appliances. We describe a removable appliance with a different spring design for proclination of more than one incisor in mixed dentition.
Materials and methods: This study is an observational study that was performed on sixteen children, 7-11 years of age, who needed incisor proclination in more than one tooth. In this study, patients were followed until the end of their orthodontic therapy. The variables evaluated were the maxillary arch length, arch depth, intercanine distance, and intermolar distance in pre- and posttreatment. To assess intra-examiner reliability, 10 plaster models were randomly selected and re-measured.
Results: In all the cases, the newly designed removable appliance was used and in all showed a significant increase in arch length, arch depth, intercanine distance, and intermolar distance. The correction was achieved within 1-9 months depending on the patient's compliance.
Conclusion: There was a significant increase in all aspects of arch length and depth after using this appliance. The procedure is a simple and effective method that is recommended for compliant patients needing proclination of more than one anterior tooth; especially in dental class III, pseudo-class III patients, and the first phase of class II division 2 skeletal treatments.
How to cite this article: Bozorgnia Y, Mafinezhad S, Pilehvar P. Introducing a Removable Orthodontic Appliance and Its Effects on Dental Arch Dimensions. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent 2021;14(S-1):S39-S43.
Keywords: Anterior dental crossbite; Malocclusion; Mixed dentition.
Copyright © 2021; Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Source of support: This work was supported by the North Khorasan University of Medical Sciences, Bojnurd, Iran (Grant No. 97/P/56). Conflict of interest: None
Figures
References
-
- Al-Sehaibany F, White G. A three dimensional clinical approach for anterior crossbite treatment in early mixed dentition using an ultrablock appliance: case report. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 1998;23(1):1–7. - PubMed
-
- American Association of Orthodontists. 2012. https://www.aaoinfo.org/system/files/media/documents/2012AAOGlossary_0.doc https://www.aaoinfo.org/system/files/media/documents/2012AAOGlossary_0.doc
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources