Effect of Alexithymia on Internet Addiction Among College Students: The Mediating Role of Metacognition Beliefs
- PMID: 35082726
- PMCID: PMC8784415
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.788458
Effect of Alexithymia on Internet Addiction Among College Students: The Mediating Role of Metacognition Beliefs
Abstract
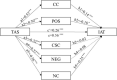
Background: Previous studies have found that alexithymia plays an important role in the pathogenesis of Internet addiction. However, the effect of alexithymia on both metacognition and Internet addiction has yet to be examined. Methods: The Toronto Alexithymia Scale, Metacognition Questionnaire, and Internet Addiction Test were used to assess a sample of 356 college students. A parallel mediator effect analysis was applied to test the hypothesis that metacognition mediates the relationship between alexithymia and Internet addiction. Results: The parallel multiple mediator models showed that alexithymia predicted the five dimensions of metacognition and Internet addiction, and that three dimensions-cognitive confidence, positive beliefs about worry, and the need to control thoughts-partially mediated this relationship. Conclusion: Alexithymia could directly and indirectly predict Internet addiction via metacognition.
Keywords: Internet addiction; alexithymia; college students; metacognition; parallel multiple mediator models.
Copyright © 2022 Luo, Zhao, Hong, Wang, Zhang and Tan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bagby M., Taylor G. (2009). “Affect dysregulation and alexithymia,” in Disorders of Affect Regulation. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

