The association between therapeutic plasma exchange and the risk of mortality among patients critically ill with COVID-19: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 35083038
- PMCID: PMC8749910
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.74972.1
The association between therapeutic plasma exchange and the risk of mortality among patients critically ill with COVID-19: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Cytokine storm has been widely known to contribute to the development of the critical condition in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), and studies had been conducted to assess the potential aspect of cytokine storm elimination by performing therapeutic plasma exchange (TPE). However, contradictory findings were observed. The objective of this study was to assess the association between TPE and the reduction of mortality of critically ill COVID-19 patients. Methods: A meta-analysis was conducted by collecting data from PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science. Data on the mortality rate of critically ill COVID-19 patients treated with TPE plus standard of care and that of patients treated with standard of care alone were analyzed using a Z test. Results: We included a total of four papers assessing the association between TPE and the risk of mortality among critically ill COVID-19 patients. Our findings suggested that critically ill COVID-19 patients treated with TPE had lower risk of mortality compared to those without TPE treatment. Conclusion: Our study has identified the potential benefits of TPE in reducing the risk of mortality among critically ill COVID-19 patients.
Keywords: COVID-19; therapeutic plasma exchange; cytokine storm; treatment.
Copyright: © 2021 Wardhani SO et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures
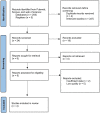

Similar articles
-
Therapeutic plasma exchange in the treatment of COVID-19 induced cytokine storm: the first Moroccan experience.BMC Infect Dis. 2023 Nov 25;23(1):829. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08816-6. BMC Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 38007416 Free PMC article.
-
Role of therapeutic plasma exchange in the management of COVID-19-induced cytokine storm syndrome.Transfus Apher Sci. 2022 Aug;61(4):103433. doi: 10.1016/j.transci.2022.103433. Epub 2022 Mar 23. Transfus Apher Sci. 2022. PMID: 35341691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic plasma exchange: A potential therapeutic modality for critically ill adults with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection.J Clin Apher. 2022 Dec;37(6):563-572. doi: 10.1002/jca.22011. Epub 2022 Sep 14. J Clin Apher. 2022. PMID: 36102158 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic plasma exchange in adults with severe COVID-19 infection.Int J Infect Dis. 2020 Oct;99:214-218. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.06.064. Epub 2020 Jun 23. Int J Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32585284 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Plasma Exchange: A potential Management Strategy for Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients.J Intensive Care Med. 2020 Sep;35(9):827-835. doi: 10.1177/0885066620940259. Epub 2020 Jul 15. J Intensive Care Med. 2020. PMID: 32666875 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Insertion/deletion (I/D) polymorphisms of angiotensin-converting enzyme gene and their implications for susceptibility and severity of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Narra J. 2024 Dec;4(3):e727. doi: 10.52225/narra.v4i3.727. Epub 2024 Dec 21. Narra J. 2024. PMID: 39816082 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of COVID-19 Treatments in Intensive Care Unit: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Crit Care Res Pract. 2024 Nov 27;2024:2973795. doi: 10.1155/ccrp/2973795. eCollection 2024. Crit Care Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 39633779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of Red Blood Cell Exchange as Adjunctive Treatment for Hypoxemia and Survival Rate of Patients With Severe Coronavirus-2 Disease: An Open-Labeled Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 8;9:899593. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.899593. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35872770 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Machine Learning in Hospitalized Patients with Severe COVID-19 Treated with Tocilizumab.J Clin Med. 2022 Aug 12;11(16):4729. doi: 10.3390/jcm11164729. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36012968 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

