Immune-Related lncRNA Pairs as Prognostic Signature and Immune-Landscape Predictor in Lung Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 35083132
- PMCID: PMC8784752
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.673567
Immune-Related lncRNA Pairs as Prognostic Signature and Immune-Landscape Predictor in Lung Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: Suppressive tumor microenvironment is closely related to the progression and poor prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). Novel individual and universal immune-related biomarkers to predict the prognosis and immune landscape of LUAD patients are urgently needed. Two-gene pairing patterns could integrate and utilize various gene expression data.
Methods: The RNA-seq and relevant clinicopathological data of the LUAD project from the TCGA and well-known immune-related genes list from the ImmPort database were obtained. Co-expression analysis followed by an analysis of variance was performed to identify differentially expressed immune-related lncRNA (irlncRNA) (DEirlncRNA) between tumor and normal tissues. Two arbitrary DEirlncRNAs (DEirlncRNAs pair) in a tumor sample underwent pairwise comparison to generate a score (0 or 1). Next, Univariate analysis, Lasso regression and Multivariate analysis were used to screen survival-related DEirlncRNAs pairs and construct a prognostic model. The Acak information standard (AIC) values of the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve for 3 years are calculated to determine the cut-off point for high- or low-risk score. Finally, we evaluated the relationship between the risk score and overall survival, clinicopathological features, immune landscape, and chemotherapy efficacy.
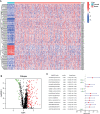
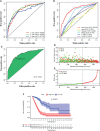
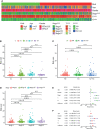
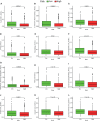
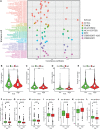
Results: Data of 54 normal and 497 tumor samples of LUAD were enrolled. After a strict screening process, 15 survival-independent-related DEirlncRNA pairs were integrated to construct a prognostic model. The AUC value of the 3-year ROC curve was 0.828. Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that patients with low risk lived longer than patients with high risk (p <0.001). Univariate and Multivariate Cox analysis suggested that the risk score was an independent factor of survival. The risk score was negatively associated with most tumor-infiltrating immune cells, immune score, and microenvironment scores. The low-risk group was correlated with increased expression of ICOS. The high-risk group had a connection with lower half inhibitory centration (IC50) of most chemotherapy drugs (e.g., etoposide, paclitaxel, vinorelbine, gemcitabine, and docetaxel) and targeted medicine-erlotinib, but with higher IC50 of methotrexate.
Conclusion: The established irlncRNA pairs-based model is a promising prognostic signature for LUAD patients. Furthermore, the prognostic signature has great potential in the evaluation of tumor immune landscape and guiding individualized treatment regimens.
Keywords: drug sensitivity; immune landscape; immune-related lncRNA pair; lung adenocarcinoma; signature.
Copyright © 2022 Yin, Zhou, Liao, Xu, Fan, Deng and Jin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of Immune-Related lncRNA Pairs and Construction and Validation of a New Prognostic Signature of Colon Cancer.Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Mar 30;2022:5827544. doi: 10.1155/2022/5827544. eCollection 2022. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35399646 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a Novel Lung Adenocarcinoma Immune-Related lncRNA Pair Signature.Int J Gen Med. 2021 Aug 11;14:4279-4289. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S325240. eCollection 2021. Int J Gen Med. 2021. PMID: 34421308 Free PMC article.
-
A novel immune-related lncRNA signature predicts the prognosis and immune landscape in ccRCC.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Mar 13;16(6):5149-5162. doi: 10.18632/aging.205633. Epub 2024 Mar 13. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38484738 Free PMC article.
-
A novel prognostic signature of immune-related lncRNA pairs in lung adenocarcinoma.Sci Rep. 2021 Aug 18;11(1):16794. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-96236-4. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34408216 Free PMC article.
-
Applying immune-related lncRNA pairs to construct a prognostic signature and predict the immune landscape of stomach adenocarcinoma.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2021 Oct;21(10):1161-1170. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2021.1962297. Epub 2021 Aug 11. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2021. PMID: 34319826
Cited by
-
Exploration of a Novel Circadian miRNA Pair Signature for Predicting Prognosis of Lung Adenocarcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 18;14(20):5106. doi: 10.3390/cancers14205106. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36291889 Free PMC article.
-
Association between white blood cell count to hemoglobin ratio and risk of in-hospital mortality in patients with lung cancer.BMC Pulm Med. 2023 Aug 18;23(1):305. doi: 10.1186/s12890-023-02600-7. BMC Pulm Med. 2023. PMID: 37596548 Free PMC article.
-
Stem cell status and prognostic applications of cuproptosis-associated lncRNAs in acute myeloid leukemia.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jan 14;12:1549294. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1549294. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 39877157 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Network National Comprehensive Cancer . Nccn Guidelines Version 2.2021 - Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer 2020. Available at: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/default_nojava.aspx. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

