Emerging Progress in Nausea and Vomiting of Pregnancy and Hyperemesis Gravidarum: Challenges and Opportunities
- PMID: 35083256
- PMCID: PMC8785858
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.809270
Emerging Progress in Nausea and Vomiting of Pregnancy and Hyperemesis Gravidarum: Challenges and Opportunities
Abstract
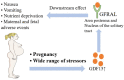
Nausea and vomiting of pregnancy (NVP) is a common condition that affects up to 70% of pregnant women. Hyperemesis gravidarum (HG) is considered the serious form of NVP, which is reported in 0.3-10.8% of pregnant women. NVP has a relatively benign course, but HG can be linked with some poor maternal, fetal, and offspring outcomes. The exact causes of NVP and HG are unknown, but various factors have been hypothesized to be associated with pathogenesis. With the advance of precision medicine and molecular biology, some genetic factors such as growth/differentiation factor 15 (GDF15) have become therapeutic targets. In our review, we summarize the historical hypotheses of the pathogenesis of NVP and HG including hormonal factors, Helicobacter pylori, gastrointestinal dysmotility, placenta-related factors, psychosocial factors, and new factors identified by genetics. We also highlight some approaches to the management of NVP and HG, including pharmacological treatment, complementary treatment, and some supporting treatments. Looking to the future, progress in understanding NVP and HG may reduce the adverse outcomes and improve the maternal quality of life during pregnancy.
Keywords: growth/differentiation factor 15; hyperemesis gravidarum; management; nausea and vomiting of pregnancy; pathophysiology.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Zhao, Qiao, Wang, He, Zhao, Fan and Jiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Jennings LK, Mahdy H. Hyperemesis Gravidarum. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls; (2021). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources