Chest X-ray versus chest computed tomography for outcome prediction in hospitalized patients with COVID-19
- PMID: 35083642
- PMCID: PMC8791092
- DOI: 10.1007/s11547-022-01456-x
Chest X-ray versus chest computed tomography for outcome prediction in hospitalized patients with COVID-19
Abstract
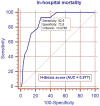
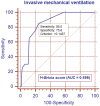
The purpose of this study was to compare the prognostic value of chest X-ray (CXR) and chest computed tomography (CT) in a group of hospitalized patients with COVID-19. For this study, we retrospectively selected a cohort of 106 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 who underwent both CXR and chest CT at admission. For each patient, the pulmonary involvement was ranked by applying the Brixia score for CXR and the percentage of well-aerated lung (WAL) for CT. The Brixia score was assigned at admission (A-Brixia score) and during hospitalization. During hospitalization, only the highest score (H-Brixia score) was considered. At admission, the percentage of WAL (A-CT%WAL) was quantified using a dedicated software. On logistic regression analyses, H-Brixia score was the most effective radiological marker for predicting in-hospital mortality and invasive mechanical ventilation. Additionally, A-CT%WAL did not provide substantial advantages in the risk stratification of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 compared to A-Brixia score.
Keywords: COVID-19; Chest X-ray; Computed tomography; SARS-CoV-2; Scoring system.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Italian Ministry of Health. COVID-19–Situation in Italy. http://www.salute.gov.it/portale/nuovocoronavirus/homeNuovoCoronavirus.jsp. Accessed 21 Oct 2021
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous