BRD4-IRF1 axis regulates chemoradiotherapy-induced PD-L1 expression and immune evasion in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 35083874
- PMCID: PMC8792480
- DOI: 10.1002/ctm2.718
BRD4-IRF1 axis regulates chemoradiotherapy-induced PD-L1 expression and immune evasion in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Chemoradiotherapy-induced PD-L1 upregulation leads to therapeutic resistance and treatment failure. The PD-1/PD-L1 blocking antibodies sensitize cancers to chemoradiotherapy by blocking extracellular PD-1 and PD-L1 binding without affecting the oncogenic function of intracellular PD-L1. Reversing the chemoradiation-induced PD-L1 expression could provide a new strategy to achieve a greater anti-tumour effect of chemoradiotherapy. Here, we aimed to identify candidate small molecular inhibitors that might boost the anti-tumour immunity of chemoradiotherapy by decreasing treatment-induced PD-L1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
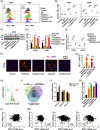
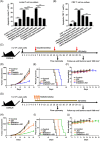
Methods: A drug array was used to recognize compounds that can suppress the cisplatin-induced and radiation-induced PD-L1 expression in NSCLC via the flow cytometry-based assay. We examined whether and how targeting bromodomain containing 4 (BRD4) inhibits chemoradiation-induced PD-L1 expression and evaluated the effect of BRD4 inhibition and chemoradiation combination in vivo.
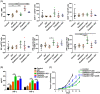
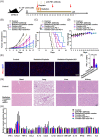
Results: BRD4 inhibitors JQ1 and ARV-771 were identified as the most promising drugs both in the cisplatin and radiation screening projects in two NSCLC cell lines. Targeting BRD4 was supposed to block chemoradiotherapy inducible PD-L1 expression by disrupting the recruitment of BRD4-IRF1 complex to PD-L1 promoter. A positive correlation between BRD4 and PD-L1 expression was observed in human NSCLC tissues. Moreover, BRD4 inhibition synergized with chemoradiotherapy and PD-1 blockade to show a robust anti-tumour immunity dependent on CD8+ T cell through limiting chemoradiation-induced tumour cell surface PD-L1 upregulation in vivo. Notably, the BRD4-targeted combinatory treatments did not show increased toxicities.
Conclusion: The data showed that BRD4-targeted therapy synergized with chemoradiotherapy and anti-PD-1 antibody by boosting anti-tumour immunity in NSCLC.
Keywords: BRD4; PD-L1; cisplatin; non-small cell lung cancer; radiotherapy.
© 2022 The Authors. Clinical and Translational Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Shanghai Institute of Clinical Bioinformatics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Miller KD, Nogueira L, Mariotto AB, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69:363‐385. - PubMed
-
- Auperin A, Le Pechoux C, Rolland E, et al. Meta‐analysis of concomitant versus sequential radiochemotherapy in locally advanced non‐small‐cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:2181‐2190. - PubMed
-
- Blackstock AW, Govindan R. Definitive chemoradiation for the treatment of locally advanced non small‐cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:4146‐4152. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
