Efficacy and safety of same-day discharge after atrial fibrillation ablation: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35084049
- PMCID: PMC8860483
- DOI: 10.1002/clc.23778
Efficacy and safety of same-day discharge after atrial fibrillation ablation: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
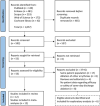
Conventionally, patients have been admitted overnight after atrial fibrillation (AF) catheter ablation. Several centers have recently adopted a same-day discharge (SDD) protocol for patients undergoing AF catheter ablation. We aimed to systematically review the current evidence for the safety and efficacy of SDD after AF catheter ablation. A systematic search was performed in PubMed, Embase, Scopus, Web of Science, and the Cochrane library until August 21, 2021. The risk of bias was assessed with the "Methodological Index for Non-Randomized Studies" (MINORS). The pooled efficacy rate of SDD protocol (defined as the proportion of patients discharged the same day of ablation among the patients who were planned for SDD) was calculated. Meanwhile, pooled major complication rates and early readmission or emergency department (ED) visit rates were evaluated in successful and planned SDD groups separately. Overall, 12 observational studies consisting of 18,065 catheter ablations were included, among which 7320 (40.52%) were discharged the same-day after ablation. The pooled efficacy was 90.3% (95% confidence interval [CI] [82.7-96.0]). The major complication rates were 1.1% (95%CI [0.5-1.9]), and 0.7% (95% CI [0.0-3.1]) in planned SDD and successful SDD groups, respectively. In addition, readmission/ED visit rate were 3.0% (95%CI [0.9-6.1]), and 3.1% (95% CI [0.8-6.5]) in the same groups. There were no significant differences between planned SDD and overnight groups with respect to major complication rate (risk ratio = 0.70, 95%CI [0.35-1.42], p-value = .369). The available data indicates that SDD after AF ablation is safe and efficient. Further prospective and randomized studies are warranted to elucidate the safety of SDD after AF ablation and develop a standardized SDD protocol.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; catheter ablation; efficacy; safety; same-day discharge.
© 2022 The Authors. Clinical Cardiology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

