Assessment of efficacy in automated plan generation for Varian Ethos intelligent optimization engine
- PMID: 35084090
- PMCID: PMC8992949
- DOI: 10.1002/acm2.13539
Assessment of efficacy in automated plan generation for Varian Ethos intelligent optimization engine
Abstract
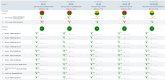
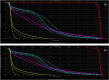
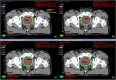
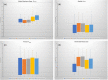
Varian Ethos, a new treatment platform, is capable of automatically generating treatment plans for initial planning and for online, adaptive planning, using an intelligent optimization engine (IOE). The primary purpose of this study is to assess the efficacy of Varian Ethos IOE for auto-planning and intercompare different treatment modalities within the Ethos treatment planning system (TPS). A total of 36 retrospective prostate and proximal seminal vesicles cases were selected for this study. The prescription dose was 50.4 Gy in 28 fractions to the proximal seminal vesicles, with a simultaneous integrated boost of 70 Gy to the prostate gland. Based on RT intent, three treatment plans were auto-generated in the Ethos TPS and were exported to the Eclipse TPS for intercomparison with the Eclipse treatment plan. When normalized for the same planning target volume (PTV) coverage, Ethos plans Dmax% were 108.1 ± 1.2%, 108.4 ± 1.6%, and 109.6 ± 2.0%, for the 9-field IMRT, 12-field IMRT, and 2-full arc VMAT plans, respectively. This compared well with Eclipse plan Dmax% values, which was 108.8 ± 1.4%. OAR indices were also evaluated for Ethos plans using Radiation Therapy Oncology Group report 0415 as a guide and were found to be comparable to each other and the Eclipse plans. While all Ethos plans were comparable, we found that, in general, the Ethos 12-field IMRT plans met most of the dosimetric goals for treatment. Also, Ethos IOE consistently generated dosimetrically hotter VMAT plans versus IMRT plans. On average, Ethos TPS took 13 min to generate 2-full arc VMAT plans, compared to 5 min for 12-field IMRT plans. Varian Ethos TPS can generate multiple treatment plans in an efficient time frame and the quality of the plans could be deemed clinically acceptable when compared to manually generated treatment plans.
Keywords: Varian Ethos; adaptive radiotherapy; auto planning; intelligent optimization engine; prostate cancer.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics published by Wiley Periodicals, LLC on behalf of The American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors claim no conflicts of interest.
Figures
 )
)
References
-
- Zarepisheh M, Long T, Li N, et al. A DVH‐guided optimization algorithm for automatic treatment planning and adaptive radiotherapy replanning. Med Phys. 2014;41:1‐14. - PubMed
-
- Chanyavanich V, Das SK, Lee WR, Lo JY. Knowledge‐based IMRT treatment planning for prostate cancer. Med Phys. 2011;38:2515‐2522. - PubMed
-
- Babier A, Mahmood R, McNiven AL, Diamant A, Chan TCY. Knowledge‐based automated planning with three‐dimensional generative adversarial networks. Med Phys. 2020;47:297‐306. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

