ICAM-1-mediated adhesion is a prerequisite for exosome-induced T cell suppression
- PMID: 35085484
- PMCID: PMC8881799
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2022.01.002
ICAM-1-mediated adhesion is a prerequisite for exosome-induced T cell suppression
Abstract
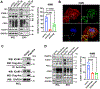
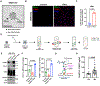
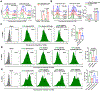
Tumor-derived extracellular vesicles (TEVs) suppress the proliferation and cytotoxicity of CD8+ T cells, thereby contributing to tumor immune evasion. Here, we report that the adhesion molecule intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) co-localizes with programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) on the exosomes; both ICAM-1 and PD-L1 are upregulated by interferon-γ. Exosomal ICAM-1 interacts with LFA-1, which is upregulated in activated T cells. Blocking ICAM-1 on TEVs reduces the interaction of TEVs with CD8+ T cells and attenuates PD-L1-mediated suppressive effects of TEVs. During this study, we have established an extracellular vesicle-target cell interaction detection through SorTagging (ETIDS) system to assess the interaction between a TEV ligand and its target cell receptor. Using this system, we demonstrate that the interaction of TEV PD-L1 with programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) on T cells is significantly reduced in the absence of ICAM-1. Our study demonstrates that ICAM-1-LFA-1-mediated adhesion between TEVs and T cells is a prerequisite for exosomal PD-L1-mediated immune suppression.
Keywords: CD8(+) T cells; ICAM-1; PD-L1; exosome; extracellular vesicles; immune suppression.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests G.D. is an employee and shareholder of NanoView Biosciences Inc.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

