The importance of accessory protein variants in the pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 35085577
- PMCID: PMC8785432
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2022.109124
The importance of accessory protein variants in the pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
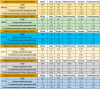
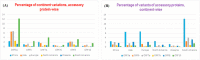
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is caused by the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS- CoV-2) with an estimated fatality rate of less than 1%. The SARS-CoV-2 accessory proteins ORF3a, ORF6, ORF7a, ORF7b, ORF8, and ORF10 possess putative functions to manipulate host immune mechanisms. These involve interferons, which appear as a consensus function, immune signaling receptor NLRP3 (NLR family pyrin domain-containing 3) inflammasome, and inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin 1β (IL-1β) and are critical in COVID-19 pathology. Outspread variations of each of the six accessory proteins were observed across six continents of all complete SARS-CoV-2 proteomes based on the data reported before November 2020. A decreasing order of percentage of unique variations in the accessory proteins was determined as ORF3a > ORF8 > ORF7a > ORF6 > ORF10 > ORF7b across all continents. The highest and lowest unique variations of ORF3a were observed in South America and Oceania, respectively. These findings suggest that the wide variations in accessory proteins seem to affect the pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: ORF10; ORF3a; ORF6; ORF7a; ORF7b; ORF8; Pathogenicity; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not have any conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures













References
-
- Boni M.F., Lemey P., Jiang X., Lam T.T., Perry B.W., Castoe T.A., Rambaut A., Robertson D.L. Evolutionary origins of the SARS-CoV-2 sarbecovirus lineage responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. Nat. Microbiol. 2020;5(11):1408–1417. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

