Investigating the Efficacy and Safety of Thalidomide for Treating Patients With ß-Thalassemia: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35087410
- PMCID: PMC8786914
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.814302
Investigating the Efficacy and Safety of Thalidomide for Treating Patients With ß-Thalassemia: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
At present, the main therapies for ß-thalassemia patients include regular blood transfusion and iron chelation, associating with a number of limitations. Thalidomide, a fetal hemoglobin (HbF) inducer that promotes γ-globin gene expression, has been reported to be effective for ß-thalassemia. Thus, this meta-analysis was conducted to assess the efficacy and safety of thalidomide for treating patients with ß-thalassemia. We searched the related studies from eight databases published from inception until December 1, 2021. The R 4.0.5 language programming was used to perform meta-analysis. After screening of retrieved articles, 12 articles were included that enrolled a total of 451 patients. The Cochrane Collaboration risk assessment tool was used to evaluate the quality and the bias risk of the randomized controlled trials (RCTs), and non randomized trials were assessed using Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS). After treatment with thalidomide, the pooled overall response rate (ORR) was 85% (95% confidence interval (CI): 80-90%), and the pooled complete response rate (CRR) was 54% (95% confidence interval: 31-76%). Compared with the placebo group, the thalidomide group had higher odds of overall response rate (odds ratio = 20.4; 95% CI: 6.75-61.64) and complete response rate (odds ratio = 20.4; 95% CI: 6.75-61.64). A statistically significant increase in hemoglobin level and HbF level after treatment, while there was no statistically significant difference in adult hemoglobin (HbA) level, spleen size, and serum ferritin. According to the results of ORR and CRR, transfusion-dependent thalassemia (TDT) patients showed remarkable efficacy of thalidomide, 83 and 52% respectively. So we analyzed 30 transfusion-dependent thalassemia patients from three studies and found that the most frequent ß-globin gene mutations were CD41-42 (-TCTT), while response to thalidomide did not show any statistically significant relationship with XmnI polymorphism or CD41-42 (-TCTT) mutation. About 30% of patients experienced mild adverse effects of thalidomide. Collectively, thalidomide is a relatively safe and effective therapy to reduce the blood transfusion requirements and to increase Hb level in patients with ß-thalassemia.
Keywords: hemoglobin level; meta-analysis; thalidomide; therapy; ß-thalassemia.
Copyright © 2022 Lu, Wei, Yang, Lai and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
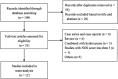
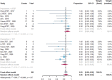



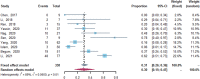
References
-
- Aerbajinai W., Zhu J., Gao Z., Chin K., Rodgers G. P. (2007). Thalidomide Induces Gamma-Globin Gene Expression through Increased Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated P38 MAPK Signaling and Histone H4 Acetylation in Adult Erythropoiesis. Blood 110 (8), 2864–2871. 10.1182/blood-2007-01-065201 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

