RapidET: a MEMS-based platform for label-free and rapid demarcation of tumors from normal breast biopsy tissues
- PMID: 35087680
- PMCID: PMC8761751
- DOI: 10.1038/s41378-021-00337-z
RapidET: a MEMS-based platform for label-free and rapid demarcation of tumors from normal breast biopsy tissues
Abstract
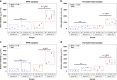
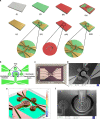
The rapid and label-free diagnosis of malignancies in ex vivo breast biopsy tissues has significant utility in pathology laboratories and operating rooms. We report a MEMS-based platform integrated with microchips that performs phenotyping of breast biopsy tissues using electrothermal sensing. The microchip, fabricated on a silicon substrate, incorporates a platinum microheater, interdigitated electrodes (IDEs), and resistance temperature detectors (RTDs) as on-chip sensing elements. The microchips are integrated onto the platform using a slide-fit contact enabling quick replacement for biological measurements. The bulk resistivity (ρ B ), surface resistivity (ρ S ), and thermal conductivity (k) of deparaffinized and formalin-fixed paired tumor and adjacent normal breast biopsy samples from N = 8 patients were measured. For formalin-fixed samples, the mean ρ B for tumors showed a statistically significant fold change of 4.42 (P = 0.014) when the tissue was heated from 25 °C to 37 °C compared to the adjacent normal tissue, which showed a fold change of 3.47. The mean ρ S measurements also showed a similar trend. The mean k of the formalin-fixed tumor tissues was 0.309 ± 0.02 W m-1 K-1 compared to a significantly higher k of 0.563 ± 0.028 W m-1 K-1 for the adjacent normal tissues. A similar trend was observed in ρ B, ρ S, and k for the deparaffinized tissue samples. An analysis of a combination of ρ B , ρ S , and k using Fisher's combined probability test and linear regression suggests the advantage of using all three parameters simultaneously for distinguishing tumors from adjacent normal tissues with higher statistical significance.
Keywords: Biosensors; Electrical and electronic engineering.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Sung H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Street, W. Cancer facts & figures 2019. 76 (American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019).
-
- Dombrowska A. Pathology meets biology: the new era of breast cancer staging. Curr. Breast Cancer Rep. 2019;11:185–189.
-
- Brender E, Burke A, Glass RM. JAMA patient page. Frozen section biopsy. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2005;294:3200. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
