Advances in Drugs Targeting Lymphangiogenesis for Preventing Tumor Progression and Metastasis
- PMID: 35087755
- PMCID: PMC8787832
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.783309
Advances in Drugs Targeting Lymphangiogenesis for Preventing Tumor Progression and Metastasis
Abstract
Metastasis of cancer cells from the primary tumor to other organs and tissues in the body is the leading cause of death in patients with malignancies. One of the principal ways cancer cells travel is through lymphatic vessels, and tumor invasion into the regional lymph nodes is a hallmark of early metastasis; thus, the formation of especially peritumoral lymphatic vessels is essential for tumor transportation that gives rise to further progression. In the past few decades, tumor-induced lymphangiogenesis has been testified to its tight correlation with lymphatic metastasis and poor clinical outcomes in multiple types of human malignancies, which warrants novel potential therapeutic targets for cancer treatment. As the understanding of underlying molecular mechanisms has grown tremendously over the years, an inexorable march of anti-lymphangiogenic therapy also aroused terrific interest. As a result, a great number of drugs have entered clinical trials, and some of them exhibited predominant contributions in cancer management. Herein, this review provides an updated summary of the current advances in therapies preventing lymphatic metastasis and discusses the validity of different applications.
Keywords: HGF; VEGF-C/-D; VEGFR-2/-3; angiogenesis; antibody; lymphangiogenesis; metastasis; tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Copyright © 2022 Wang and Chu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
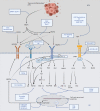
Figures
References
-
- Cohen MH, Gootenberg J, Keegan P, Pazdur R. FDA Drug Approval Summary: Bevacizumab (Avastin) Plus Carboplatin and Paclitaxel as First-Line Treatment of Advanced/Metastatic Recurrent Nonsquamous non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncologist (2007) 12(6):713–8. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.12-6-713 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

