Development of a Spontaneous HPV16 E6/E7-Expressing Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma in HLA-A2 Transgenic Mice
- PMID: 35089069
- PMCID: PMC8725581
- DOI: 10.1128/mbio.03252-21
Development of a Spontaneous HPV16 E6/E7-Expressing Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma in HLA-A2 Transgenic Mice
Erratum in
-
Erratum for Peng et al., "Development of a Spontaneous HPV16 E6/E7-Expressing Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma in HLA-A2 Transgenic Mice".mBio. 2022 Apr 26;13(2):e0029622. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00296-22. Epub 2022 Mar 1. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35229636 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
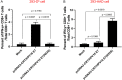
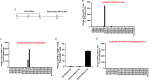
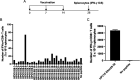
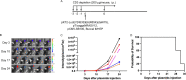
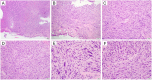
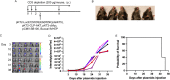
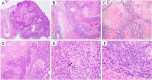
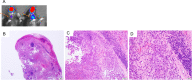
Human papillomavirus (HPV)-associated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is a growing global health problem. HPV16 has been attributed to a majority of HPV-associated HNSCCs. In order to test candidate immunotherapies, we developed a spontaneous HPV16-driven HNSCC model in HLA-A2 (AAD) transgenic mice. We sought to eliminate the confounding effects of dominant HPV antigen presentation through murine major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) via epitope mutagenesis (without compromising tumorigenicity). We generated HPV16 E6(R55K)(delK75) and E7(N53S) expression constructs with mutations in known dominant H-2Db epitopes and characterized their presentation through murine and human MHC-I molecules using in vitro and in vivo activation of HPV16 E6/E7 antigen-specific CD8+ T cells. In addition, we tested the ability of E6(R55K)(delK75) and E7(N53S) for oncogenicity. The mutated E7(N53S) abolished the presentation of murine H-2Db-restricted HPV16 E7 peptide (i.e., amino acids [aa] 49 to 57) cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) epitope and resulted in HLA-A2-restricted presentation of the HPV16 E7 (aa 11 to 20)-specific CTL epitope. The mutated E6(R55K)(delK75) abolished the activation of murine MHC-I-restricted E6-specific CD8+ T cell-mediated immune responses in C57BL/6 mice. In addition, the vaccination led to the activation of human HLA-A2-restricted E6-specific CD8+ T cell-mediated immune responses in HLA-A2 (AAD) transgenic mice. Injection of DNA plasmids encoding LucE7(N53S)E6(R55K)(delK75), AKT, c-Myc, and SB100 followed by electroporation results in development of squamous cell carcinoma in the oral/pharyngeal cavity of all of the HLA-A2 (AAD) transgenic mice (5/5), with 2/5 tumor-bearing mice developing metastatic carcinoma in the neck lymph nodes. IMPORTANCE Our data indicate that mutated HPV16 E6(R55K)(delK75) and mutated HPV16 E7(N53S) DNA abolishes the presentation of HPV16 E6 and E7 through murine MHC-I and results in their presentation through human HLA-A2 molecules. Additionally, the mutated HPV16 E6 and E7 remain oncogenic. Our approach is potentially applicable to different human MHC-I transgenic mice for the identification of human MHC-I restricted HPV16 E6/E7-specific CTL epitopes as well as the generation of spontaneous HPV E6/E7-expressing oral/pharyngeal carcinoma.
Keywords: E6; E7; HPV16; OPSCC; human papillomavirus; oral tumor model.
Conflict of interest statement
T.-C. Wu and Richard B. S. Roden are cofounders of and have an equity ownership interest in Papivax LLC. Also, both own Papivax Biotech, Inc., stock and are members of the Scientific Advisory Board of Papivax Biotech, Inc. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of human MHC-I HPV18 E6/E7-specific CD8 + T cell epitopes and generation of an HPV18 E6/E7-expressing adenosquamous carcinoma in HLA-A2 transgenic mice.J Biomed Sci. 2022 Oct 12;29(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s12929-022-00864-5. J Biomed Sci. 2022. PMID: 36224625 Free PMC article.
-
Control of Spontaneous HPV16 E6/E7 Expressing Oral Cancer in HLA-A2 (AAD) Transgenic Mice with Therapeutic HPV DNA Vaccine.J Biomed Sci. 2021 Sep 13;28(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s12929-021-00759-x. J Biomed Sci. 2021. PMID: 34517865 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of HLA-A2-restricted HPV-16 E7-specific CD8(+) T-cell immune responses induced by DNA vaccines in HLA-A2 transgenic mice.Gene Ther. 2006 Jan;13(1):67-77. doi: 10.1038/sj.gt.3302607. Gene Ther. 2006. PMID: 16107858 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the roles of HPV16 variants in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: current challenges and opportunities.Virol J. 2021 Nov 8;18(1):217. doi: 10.1186/s12985-021-01688-9. Virol J. 2021. PMID: 34749746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From infection to immortality: The role of HPV and telomerase in head and neck cancer.Oral Oncol. 2025 Feb;161:107169. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2024.107169. Epub 2025 Jan 3. Oral Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39755000 Review.
Cited by
-
A replicative recombinant HPV16 E7 expression virus upregulates CD36 in C33A cells.Front Microbiol. 2023 Aug 30;14:1259510. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1259510. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37795297 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and Dynamic-Based Characterization of the Recognition Patterns of E7 and TRP-2 Epitopes by MHC Class I Receptors through Computational Approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 23;25(3):1384. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031384. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338663 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of human MHC-I HPV18 E6/E7-specific CD8 + T cell epitopes and generation of an HPV18 E6/E7-expressing adenosquamous carcinoma in HLA-A2 transgenic mice.J Biomed Sci. 2022 Oct 12;29(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s12929-022-00864-5. J Biomed Sci. 2022. PMID: 36224625 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the immunological landscape and emerging immunotherapeutic strategies in cervical cancer: a comprehensive review.Front Oncol. 2025 Jul 10;15:1620501. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1620501. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40708940 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lewis A, Kang R, Levine A, Maghami E. 2015. The new face of head and neck cancer: the HPV epidemic. Oncology (Williston Park) 29:616–626. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

