A comparison of the associations between bone health and three different intensities of accelerometer-derived habitual physical activity in children and adolescents: a systematic review
- PMID: 35089364
- PMCID: PMC9106641
- DOI: 10.1007/s00198-021-06218-5
A comparison of the associations between bone health and three different intensities of accelerometer-derived habitual physical activity in children and adolescents: a systematic review
Erratum in
-
Correction: A comparison of the associations between bone health and three different intensities of accelerometer-derived habitual physical activity in children and adolescents: a systematic review.Osteoporos Int. 2022 Jun;33(6):1413. doi: 10.1007/s00198-022-06362-6. Osteoporos Int. 2022. PMID: 35348838 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
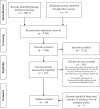
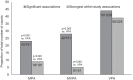
Positive associations have been identified between bone outcomes and accelerometer-derived moderate (MPA) and vigorous (VPA) physical activity (PA) in youth; however, it remains unclear which intensity is most beneficial. This systematic review aimed to summarise accelerometer-derived methods used to estimate habitual PA in children and adolescents and determine whether the magnitude of association was consistently stronger for a particular intensity (MPA/MVPA/VPA). Observational studies assessing associations between accelerometer-derived MPA and/or MVPA and VPA with bone outcomes in children and adolescents (≤ 18 years) were identified in MEDLINE, EMBASE, Web of Science, SPORTDiscus and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials. Thirty articles were included (total n = 20,613 (10,077 males), 4-18 years). Chi-square tests determined whether the proportion of significant associations and strongest within-study associations differed significantly between intensities. Results demonstrated that accelerometer methods were highly variable between studies. Of the 570 associations analysed, 186 were significant (p < 0.05). The proportion of within-study strongest associations differed by PA intensity (3 × 2 χ2 = 86.6, p < 0.001) and was significantly higher for VPA (39%) compared to MVPA (5%; 2 × 2 χ2 = 55.3, p < 0.001) and MPA (9%, 2 × 2 χ2 = 49.1, p < 0.001). Results indicated a greater benefit of VPA over MPA/MVPA; however, variability in accelerometer-derived methods used prevents the precise bone-benefitting amount of VPA from being identified. Long epochs and numerous intensity cut-point definitions mean that bone-relevant PA has likely been missed or misclassified in this population. Future research should explore the use of shorter epochs (1 s) and identify bone-specific activity intensities, rather than using pre-defined activity classifications more relevant to cardiovascular health.
Keywords: Accelerometry; Bone; Children; Physical activity.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

