OX40L Inhibition Suppresses KLH-driven Immune Responses in Healthy Volunteers: A Randomized Controlled Trial Demonstrating Proof-of-Pharmacology for KY1005
- PMID: 35092305
- PMCID: PMC9314635
- DOI: 10.1002/cpt.2539
OX40L Inhibition Suppresses KLH-driven Immune Responses in Healthy Volunteers: A Randomized Controlled Trial Demonstrating Proof-of-Pharmacology for KY1005
Abstract
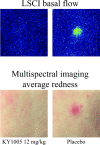
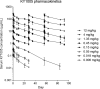
The safety, tolerability, immunogenicity, and pharmacokinetic (PK) profile of an anti-OX40L monoclonal antibody (KY1005, currently amlitelimab) were evaluated. Pharmacodynamic (PD) effects were explored using keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH) and tetanus toxoid (TT) immunizations. Sixty-four healthy male subjects (26.5 ± 6.0 years) were randomized to single doses of 0.006, 0.018, or 0.05 mg/kg, or multiple doses of 0.15, 0.45, 1.35, 4, or 12 mg/kg KY1005, or placebo (6:2). Serum KY1005 concentrations were measured. Antibody responses upon KLH and TT immunizations and skin response upon intradermal KLH administration were performed. PD data were analyzed using repeated measures analysis of covariances (ANCOVAs) and post hoc exposure-response modeling. No serious adverse events occurred and all adverse events were temporary and of mild or moderate severity. A nonlinear increase in mean serum KY1005 concentrations was observed (median time to maximum concentration (Tmax ) ~ 4 hours, geometric mean terminal half-life (t½) ~ 24 days). Cutaneous blood perfusion (estimated difference (ED) -13.4 arbitrary unit (AU), 95% confidence interval (CI) -23.0 AU to -3.8 AU) and erythema quantified as average redness (ED -0.23 AU, 95% CI -0.35 AU to -0.11 AU) decreased after KY1005 treatment at doses of 0.45 mg/kg and above. Exposure-response analysis displayed a statistically significant treatment effect on anti-KLH antibody titers (IgG maximum effect (Emax ) -0.58 AU, 95% CI -1.10 AU to -0.06 AU) and skin response (erythema Emax -0.20 AU, 95% CI -0.29 AU to -0.11 AU). Administration of KY1005 demonstrated an acceptable safety and tolerability profile and PK analyses displayed a nonlinear profile of KY1005. Despite the observed variability, skin challenge response after KY1005 treatment indicated pharmacological activity of KY1005. Therefore, KY1005 shows potential as a novel pharmacological treatment in immune-mediated disorders.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03161288.
© 2022 The Authors. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
J.P., S.G., M.Y., B.P.B., N.B., S.Q., and R.W. are employed by the sponsor. All other authors declared no competing interests for this work.
Figures


References
-
- Baumann, R. , Yousefi, S. , Simon, D. , Russmann, S. , Mueller, C. & Simon, H.‐U. Functional expression of CD134 by neutrophils. Eur. J. Immunol. 34, 2268–2275 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Gramaglia, I. , Jember, A. , Pippig, S.D. , Weinberg, A.D. , Killeen, N. & Croft, M. The OX40 costimulatory receptor determines the development of CD4 memory by regulating primary clonal expansion. J. Immunol. 165, 3043–3050 (2000). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

