Kynurenine pathway in Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): Potential role in prognosis
- PMID: 35092710
- PMCID: PMC8906035
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.24257
Kynurenine pathway in Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): Potential role in prognosis
Abstract
Background: It is known that inflammatory responses play an important role in the pathophysiology of COVID-19.
Aims: In this study, we aimed to examine the role of kynurenine (KYN) metabolism on the severity of COVID-19 disease AQ5.
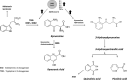
Materials & methods: Seventy COVID-19 patients of varying severity and 30 controls were included in the study. In addition to the classical laboratory parameters, KYN, tryptophan (TRP), kynurenic acid (KYNA), 3 hydroxykynurenine (3OHKYN), quinolinic acid (QA), and picolinic acid (PA) were measured with mass spectrometry.
Results: TRP, KYN, KYN:TRP ratio, KYNA, 3OHKYN, PA, and QA results were found to be significantly different in COVID-19 patients (p < 0.001 for all). The KYN:TRP ratio and PA of severe COVID-19 patients was statistically higher than that of mild-moderate COVID-19 patients (p < 0.001 for all). When results were examined, statistically significant correlations with KYN:TRP ratio, IL-6, ferritin, and procalcitonin were only found in COVID-19 patients. ROC analysis indicated that highest AUC values were obtained by KYN:TRP ratio and PA (0.751 vs 0.742). In determining the severity of COVID-19 disease, the odd ratios (and confidence intervals) of KYN:TRP ratio and PA levels that were adjusted according to age, gender, and comorbidity were determined to be 1.44 (1.1-1.87, p = 0.008) and 1.06 (1.02-1.11, p = 0.006), respectively.
Discussion & conclusion: According to the results of this study, KYN metabolites play a role in the pathophysiology of COVID-19, especially KYN:TRP ratio and PA could be markers for identification of severe COVID-19 cases.
Keywords: coronavirus-19 disease (COVID-19); kynurenine pathway; prognosis.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

