Renal denervation for atrial fibrillation: a comprehensive updated systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35094013
- PMCID: PMC9553644
- DOI: 10.1038/s41371-022-00658-0
Renal denervation for atrial fibrillation: a comprehensive updated systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
The study aims to compare clinical outcomes following renal denervation (RDN) in hypertensive patients with atrial fibrillation (AF). Three online databases were searched (MEDLINE, EMBASE and PubMed) for literature related to outcomes of RDN on hypertension and AF, between January 1, 2010, and June 1, 2021. Where possible, risk ratios (RR) and mean differences (MD) were combined using a random effects model. Significance was set at p ≤ 0.05. Seven trials were included that assessed the effect of adding RDN to pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) in patients with hypertension and AF. A total of 711 patients (329 undergoing PVI + RDN and 382 undergoing PVI alone), with an age range of 56 ± 6 to 68 ± 9 years, were included. Pooled analysis showed a significant lowering of AF recurrence in the PVI + RDN (31.3%) group compared to the PVI-only (52.9%) group (p < 0.00001). Pooled analysis of patients with resistant hypertension showed a significant mean reduction of systolic blood pressure (SBP) (-9.42 mm Hg, p = 0.05), but not diastolic blood pressure (DBP) (-4.11 mm Hg, p = 0.16) in favor of PVI + RDN. Additionally, the pooled analysis showed that PVI + RDN significantly improved estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) (+10.2 mL/min per 1.73 m2, p < 0.001) compared to PVI alone. RDN procedures in these trials have proven to be both safe and efficacious with an overall complication rate of 6.32%. Combined PVI and RDN is beneficial for patients with hypertension and AF. Combined therapy showed improvement in SBP and eGFR, reducing the risk of AF recurrence. RDN may serve as an innovative intervention in the treatment of AF.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
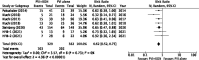


Comment in
-
Renal denervation for atrial fibrillation: the issue of bias due to nonblinding.J Hum Hypertens. 2023 Jan;37(1):88. doi: 10.1038/s41371-022-00699-5. Epub 2022 Apr 22. J Hum Hypertens. 2023. PMID: 35459789 No abstract available.
-
Renal denervation for atrial fibrillation: a comprehensive updated systematic review and meta-analysis.J Hum Hypertens. 2023 Jan;37(1):89-90. doi: 10.1038/s41371-022-00700-1. Epub 2022 Apr 25. J Hum Hypertens. 2023. PMID: 35469058 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lloyd-Jones D, Adams RJ, Brown TM, Carnethon M, Dai S, De Simone G, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2010 Update. Circulation. 2010;121. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.192667. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

