An Impending Paradigm Shift in Motor Imagery Based Brain-Computer Interfaces
- PMID: 35095410
- PMCID: PMC8789741
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2021.824759
An Impending Paradigm Shift in Motor Imagery Based Brain-Computer Interfaces
Abstract
The development of reliable assistive devices for patients that suffer from motor impairments following central nervous system lesions remains a major challenge in the field of non-invasive Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs). These approaches are predominated by electroencephalography and rely on advanced signal processing and machine learning methods to extract neural correlates of motor activity. However, despite tremendous and still ongoing efforts, their value as effective clinical tools remains limited. We advocate that a rather overlooked research avenue lies in efforts to question neurophysiological markers traditionally targeted in non-invasive motor BCIs. We propose an alternative approach grounded by recent fundamental advances in non-invasive neurophysiology, specifically subject-specific feature extraction of sensorimotor bursts of activity recorded via (possibly magnetoencephalography-optimized) electroencephalography. This path holds promise in overcoming a significant proportion of existing limitations, and could foster the wider adoption of online BCIs in rehabilitation protocols.
Keywords: Brain-Computer Interface (BCI); EEG; beta bursts; magnetoencephalography (MEG); motor imagery (MI); neurological rehabilitation; upper limb.
Copyright © 2022 Papadopoulos, Bonaiuto and Mattout.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
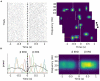
Figures

References
-
- Anderson R. W., Kehnemouyi Y. M., Neuville R. S., Wilkins K. B., Anidi C. M., Petrucci M. N., et al. (2020). A novel method for calculating beta band burst durations in Parkinson’s disease using a physiological baseline. J. Neurosci. Methods 343:108811. 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2020.108811 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blankertz B., Tomioka R., Lemn S., Kawanabe M., Muller K.-R. (2008). Optimizing spatial filters for robust EEG single-trial analysis. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 25 41–56.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

