Vindoline Attenuates Osteoarthritis Progression Through Suppressing the NF-κB and ERK Pathways in Both Chondrocytes and Subchondral Osteoclasts
- PMID: 35095488
- PMCID: PMC8790248
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.764598
Vindoline Attenuates Osteoarthritis Progression Through Suppressing the NF-κB and ERK Pathways in Both Chondrocytes and Subchondral Osteoclasts
Abstract
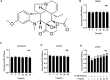
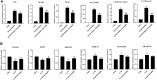
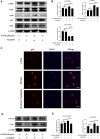
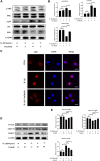
Disruption of extracellular matrix (ECM) homeostasis and subchondral bone remodeling play significant roles in osteoarthritis (OA) pathogenesis. Vindoline (Vin), an indole alkaloid extracted from the medicinal plant Catharanthus roseus, possesses anti-inflammatory properties. According to previous studies, inflammation is closely associated with osteoclast differentiation and the disorders of the homeostasis between ECM. Although Vin has demonstrated effective anti-inflammatory properties, its effects on the progression of OA remain unclear. We hypothesized that Vin may suppress the progress of OA by suppressing osteoclastogenesis and stabilizing ECM of articular cartilage. Therefore, we investigated the effects and molecular mechanisms of Vin as a treatment for OA in vitro and in vivo. In the present study, we found that Vin significantly suppressed RANKL-induced osteoclast formation and obviously stabilized the disorders of the ECM homeostasis stimulated by IL-1β in a dose-dependent manner. The mRNA expressions of osteoclast-specific genes were inhibited by Vin treatment. Vin also suppressed IL-1β-induced mRNA expressions of catabolism and protected the mRNA expressions of anabolism. Moreover, Vin notably inhibited the activation of RANKL-induced and IL-1β-induced NF-κB and ERK pathways. In vivo, Vin played a protective role by inhibiting osteoclast formation and stabilizing cartilage ECM in destabilization of the medial meniscus (DMM)-induced OA mice. Collectively, our observations provide a molecular-level basis for Vin's potential in the treatment of OA.
Keywords: ERK pathway; NF-κB pathway; extracellular matrix; osteoarthritis; osteoclastogenesis; vindoline.
Copyright © 2022 Zhu, Xu, Yang, Zhan, Zhang, Liu and Dai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Amentoflavone maintaining extracellular matrix homeostasis and inhibiting subchondral bone loss in osteoarthritis by inhibiting ERK, JNK and NF-κB signaling pathways.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Oct 15;19(1):662. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-05075-2. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 39407273 Free PMC article.
-
VX-11e protects articular cartilage and subchondral bone in osteoarthritis by inhibiting the RIP1/RIP3/MLKL and MAPK signaling pathways.Bioorg Chem. 2022 Mar;120:105632. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.105632. Epub 2022 Jan 19. Bioorg Chem. 2022. PMID: 35074577
-
Paroxetine Attenuates Chondrocyte Pyroptosis and Inhibits Osteoclast Formation by Inhibiting NF-κB Pathway Activation to Delay Osteoarthritis Progression.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023 Aug 16;17:2383-2399. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S417598. eCollection 2023. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023. PMID: 37605762 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin attenuates osteoclast-mediated abnormal subchondral bone remodeling and alleviates osteoarthritis via AMPK/NF-κB/ERK signaling pathway.PLoS One. 2021 Dec 16;16(12):e0261127. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0261127. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34914744 Free PMC article.
-
PD0325901, an ERK inhibitor, attenuates RANKL-induced osteoclast formation and mitigates cartilage inflammation by inhibiting the NF-κB and MAPK pathways.Bioorg Chem. 2023 Mar;132:106321. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.106321. Epub 2022 Dec 30. Bioorg Chem. 2023. PMID: 36642020
Cited by
-
Vindoline is a key component of Catharanthus roseus leaf juice extract prepared through an Ayurveda-based method for ameliorating insulin-resistant type 2 diabetes.Protoplasma. 2025 May;262(3):667-681. doi: 10.1007/s00709-024-02026-w. Epub 2025 Jan 11. Protoplasma. 2025. PMID: 39794517
-
Pulchinenoside C Attenuates the Development of Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB Signalling Pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Aug;29(15):e70738. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70738. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40746264 Free PMC article.
-
Zhuifeng tougu capsules inhibit the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway and alleviate knee osteoarthritis: In vitro and in vivo experiments.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 15;13:951860. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.951860. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36188596 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D Alleviates Osteoarthritis Progression by Targeting Cartilage and Subchondral Bone via Myd88-TAK1-ERK Axis Suppression.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Jul 8;19:5855-5870. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S526064. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40657039 Free PMC article.
-
A bibliometric analysis of studies related to the nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathway in knee osteoarthritis between 2004 and 2023.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 25;12:1572161. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1572161. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40636390 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

