Paeonol Ameliorates Chronic Itch and Spinal Astrocytic Activation via CXCR3 in an Experimental Dry Skin Model in Mice
- PMID: 35095512
- PMCID: PMC8794748
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.805222
Paeonol Ameliorates Chronic Itch and Spinal Astrocytic Activation via CXCR3 in an Experimental Dry Skin Model in Mice
Abstract
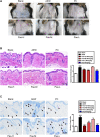
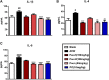
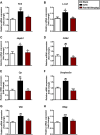
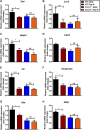
Paeonol is a bioactive phenol presents mainly in Paeonia suffruticosa Andr. (Paeoniaceae), Paeonia lactiflora Pall., and Dioscorea japonica Thunb. (Dioscoreaceae), harboring various pharmacological activities including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, immune regulatory activity and reverse chemoresistance. Recent reports revealed paeonol exhibited good effects on chronic dermatitis, such as atopic dermatitis (AD) and psoriasis. However, whether paeonol is effective for dry skin disease and its mechanism of action still remain unclear. In this study, we analysed the effects of paeonol on a mouse model of dry skin treated with acetone-ether-water (AEW), which showed impressive activities in reducing scratching behavior and skin inflammation. To elucidate the underlying molecular targets for the anti-pruritic ability of paeonol, we screened the expression of possible chemokine pathways in the spinal cord. The expression of CXCR3 was significantly alleviated by paeonol, which increased greatly in the spinal neurons of AEW mice. In addition, treatment of paeonol significantly inhibited AEW-induced expression of astrocyte activity-dependent genes including Tlr4, Lcn2 and Hspb1 et al. The inhibitory effects of paeonol on scratching behavior and astrocytic activation in the spinal cord induced by AEW were abolished when CXCR3 was antagonized or genetically ablated. Taken together, our results indicated that paeonol can ameliorate AEW-induced inflammatory response and itching behavior, and reduce the expression of spinal astrocyte activity-dependent genes induced by AEW, which are driven by CXCR3.
Keywords: AEW; CXCR3; anti-pruritic; astrocyte; inflammation; paeonol.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Li, Zhao, Liu, Wang, Xiong and Mei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Chemokine Receptor CXCR3 in the Spinal Cord Contributes to Chronic Itch in Mice.Neurosci Bull. 2018 Feb;34(1):54-63. doi: 10.1007/s12264-017-0128-z. Epub 2017 Apr 11. Neurosci Bull. 2018. PMID: 28401489 Free PMC article.
-
Spinal histamine H4 receptor mediates chronic pruritus via p-ERK in acetone-ether-water (AEW)-induced dry skin mice.Exp Dermatol. 2024 Jul;33(7):e15128. doi: 10.1111/exd.15128. Exp Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38973249
-
Spinal cord NLRP1 inflammasome contributes to dry skin induced chronic itch in mice.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Apr 20;17(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01807-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 32312281 Free PMC article.
-
Paeonol Derivatives and Pharmacological Activities: A Review of Recent Progress.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2020;20(6):466-482. doi: 10.2174/1389557519666191015204223. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31644406 Review.
-
Chemistry, pharmacokinetics, pharmacology and recent novel drug delivery systems of paeonol.Life Sci. 2020 Jun 1;250:117544. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117544. Epub 2020 Mar 13. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32179072 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioactive Metabolites of Dioscorea Species and Their Potential Applications in Functional Food Development.Foods. 2025 Jul 20;14(14):2537. doi: 10.3390/foods14142537. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40724357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and Key Materials of East Asian Herbal Medicine Combined with Conventional Medicine on Inflammatory Skin Lesion in Patients with Psoriasis Vulgaris: A Meta-Analysis, Integrated Data Mining, and Network Pharmacology.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Aug 15;16(8):1160. doi: 10.3390/ph16081160. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37631075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Paeonol alleviates placental inflammation and apoptosis in preeclampsia by inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2022 Nov;38(11):1103-1112. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12585. Epub 2022 Aug 24. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 36054229 Free PMC article.
-
Dioscorea spp.: Bioactive Compounds and Potential for the Treatment of Inflammatory and Metabolic Diseases.Molecules. 2023 Mar 22;28(6):2878. doi: 10.3390/molecules28062878. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36985850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Annexin 1 Reduces Dermatitis-Induced Itch and Cholestatic Itch through Inhibiting Neuroinflammation and Iron Overload in the Spinal Dorsal Horn of Mice.Brain Sci. 2024 Apr 28;14(5):440. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14050440. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 38790419 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

