Effects of Exogenous Hydrogen Sulfide in the Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus on Gastric Function in Rats
- PMID: 35095514
- PMCID: PMC8793780
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.806012
Effects of Exogenous Hydrogen Sulfide in the Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus on Gastric Function in Rats
Abstract
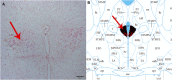
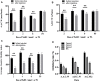
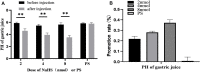
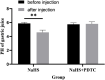
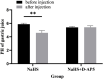
Background: Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is a new type of gas neurotransmitter discovered in recent years. It plays an important role in various physiological activities. The hypothalamus paraventricular nucleus (PVN) is an important nucleus that regulates gastric function. This study aimed to clarify the role of H2S in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus on the gastric function of rats. Methods: An immunofluorescence histochemistry double-labelling technique was used to determine whether cystathionine-beta-synthase (CBS) and c-Fos neurons are involved in PVN stress. Through microinjection of different concentrations of NaHS, physiological saline (PS), D-2-Amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid (D-AP5), and pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC), we observed gastric motility and gastric acid secretion. Results: c-Fos and CBS co-expressed the most positive neurons after 1 h of restraint and immersion, followed by 3 h, and the least was at 0 h. After injection of different concentrations of NaHS into the PVN, gastric motility and gastric acid secretion in rats were significantly inhibited and promoted, respectively (p < 0.01); however, injection of normal saline, D-AP5, and PDTC did not cause any significant change (p > 0.05). The suppressive effect of NaHS on gastrointestinal motility and the promotional effect of NaHS on gastric acid secretion could be prevented by D-AP5, a specific N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA) receptor antagonist, and PDTC, an NF-κB inhibitor. Conclusion: There are neurons co-expressing CBS and c-Fos in the PVN, and the injection of NaHS into the PVN can inhibit gastric motility and promote gastric acid secretion in rats. This effect may be mediated by NMDA receptors and the NF-κB signalling pathway.
Keywords: CBS (cystathionine β-lyase); gastric acid secretion; gastric motility; hydrogen sulfide; hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN).
Copyright © 2022 Li, Sun, Shi, Yu, Ji, Li, Zhou, Liu, Xue and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effect of exogenous hydrogen sulfide in the nucleus tractus solitarius on gastric motility in rats.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Aug 7;29(29):4557-4570. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i29.4557. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37621756 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the L-Glu-NMDA receptor-H2S-NMDA receptor pathway that regulates gastric function in rats' nucleus ambiguus.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 1;15:1389873. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1389873. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38751777 Free PMC article.
-
Exogenous Hydrogen Sulfide Within the Nucleus Ambiguus Inhibits Gastrointestinal Motility in Rats.Front Physiol. 2020 Sep 11;11:545184. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.545184. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33013478 Free PMC article.
-
Role of hydrogen sulfide within the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus in the control of gastric function in rats.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015 May;27(5):618-26. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12530. Epub 2015 Mar 14. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015. PMID: 25773343
-
Role of hydrogen sulfide in secondary neuronal injury.Neurochem Int. 2014 Jan;64:37-47. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2013.11.002. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Neurochem Int. 2014. PMID: 24239876 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of exogenous hydrogen sulfide in the nucleus tractus solitarius on gastric motility in rats.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Aug 7;29(29):4557-4570. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i29.4557. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37621756 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of microRNAs and the microRNA-messengerRNA regulatory network in chronic alcohol exposure.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 21;15:1377501. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1377501. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39234114 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the L-Glu-NMDA receptor-H2S-NMDA receptor pathway that regulates gastric function in rats' nucleus ambiguus.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 1;15:1389873. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1389873. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38751777 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) Generated in the Colon Induces Neuropathic Pain by Activating Spinal NMDA Receptors in a Rodent Model of Chronic Constriction Injury.Neurochem Res. 2025 Jan 30;50(2):90. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04342-w. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 39883291
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

